The Federal Assessment Standards indicate 3 dates:
- Valuation date – the date as of which the value of the object was determined;
- Inspection date – the date of the actual inspection of the property. If intangible things are assessed (intangible assets, bonds or bills, rights of claim), then an inspection is not carried out and this item is not included in the Report.
- Date of preparation of the report – date of issue and signing of the Report. The validity period of the Report is 6 months, it is calculated from the date of preparation.
Difference between modern and retrospective assessment
The assessment can be carried out as of the current date or as of a date in the past. In the first case, the appraiser goes to the site and records its characteristics for today. Later, when drawing up the Report, he:
- attaches current photographs of the object;
- provides identification data - location address, inventory number, vin number, etc.;
- describes the current state of the object;
- provides a description of the identified defects;
- attaches an inspection report drawn up at the time of visiting the property and certified by the owner.
When determining the current value, it is important that the date of assessment coincides with the date of inspection of the property. Only in this case the result can be considered reliable.
However, you may often find that the inspection is carried out before or after the valuation date. What does this mean?
If the inspection was carried out before the date of assessment, then at the time of the actual work it may no longer physically exist. For example, the appraiser inspected the house on the 10th, and the next day there was a fire that completely destroyed the building. If the appraisal company makes calculations on the 11th, the data will be unreliable - after all, there is nothing to evaluate in fact.
When an inspection is carried out after the date of assessment, the specialist may not take into account any changes made. For example, an appraiser calculated the cost of an apartment on the 10th, and the owner decided to increase its market price by replacing the windows with new ones. The replacement work was carried out on the 11th, the appraiser will come for inspection on the 12th and, accordingly, will no longer take into account the changes made.
A retrospective appraisal is a calculation of the value of an object at a date in the past. In this case, the inspection is carried out on the current date. This type of assessment is carried out for the following purposes:
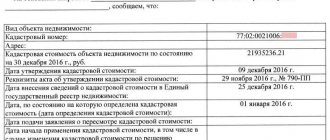
- Challenging the cadastral value.
- Entry into inheritance rights.
- Litigation.
For example, quite often there are cases when, during the consideration of a case in court, a specific date is fixed. Let's say the date of the transaction between the plaintiff and the defendant. Although the trial may last several years, the assessment date will remain the same.
Disputes regarding the value of real estate are quite common. The plaintiff may claim that the property was sold several years ago at an inadequate price. In this case, a retrospective revaluation of the property will be carried out on the date of the transaction.
Case study: we conducted an assessment in 2010. In 2020, they decided to challenge the transaction carried out with the help of our Report, and the date of assessment in the Report of our opponents remained unchanged - still 2010, although they carried out the assessment 8 years later.
Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation
Order
September 25, 2014 No. 611
On approval of the Federal Valuation Standard “Real Estate Valuation (FSO No. 7)” In accordance with Article 20 of the Federal Law of July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ “On Valuation Activities in the Russian Federation” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 1998, No. 31, Art. 3813; 2006, No. 31, Art. 3456; 2010, No. 30, Art. 3998; 2011, No. 1, Art. 43; No. 29, Art. 4291; 2014, No. 30, Art. 4226) I order:
Approve the attached Federal Valuation Standard “Real Estate Valuation (FSO No. 7)”. Minister A.V. Ulyukaev
APPROVED by order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated September 25, 2014 No. 611
Federal Valuation Standard “Real Estate Valuation (FSO No. 7)”
I. General provisions
1. This Federal Valuation Standard has been developed taking into account international valuation standards and federal valuation standards “General concepts of valuation, approaches to valuation and requirements for valuation (FSO No. 1)”, “Purpose of valuation and types of value (FSO No. 2)”, “ Requirements for an assessment report (FSO No. 3)” (hereinafter referred to as FSO No. 1, FSO No. 2, FSO No. 3) and defines the requirements for conducting a real estate assessment.
2. This Federal Valuation Standard develops, supplements and specifies the requirements and procedures established by FSO No. 1, FSO No. 2, FSO No. 3, and is mandatory for use when appraising real estate.
3. The provisions of this Federal Valuation Standard do not apply to the valuation of aircraft and sea vessels, inland navigation vessels, space objects, subsoil plots, enterprises as property complexes subject to state registration, as well as to the determination of the cadastral value of real estate using mass valuation methods.
II. Objects of assessment
4. For the purposes of this Federal Standard, the objects of assessment may be real estate objects - developed land plots, undeveloped land plots, capital construction projects, as well as parts of land plots and capital construction projects, residential and non-residential premises, together or separately, taking into account related their property rights, if this does not contradict current legislation. For the purposes of this Federal Standard, the objects of valuation may be shares in the right to real estate.
III. General requirements for conducting an assessment
5. When collecting information about the property being appraised, the appraiser or his representative conducts an inspection of the property being appraised during a period possibly close to the appraisal date, unless otherwise specified in the appraisal assignment. In case of failure to conduct an inspection, the appraiser indicates in the evaluation report the reasons why the object of assessment was not inspected, as well as assumptions and limitations associated with the failure to conduct an inspection.
6. A joint assessment of a land plot and capital construction projects located on it in the absence of title and title documents for the land plot is carried out taking into account the rights and obligations of the owner of capital construction projects in relation to the land plot established by current legislation, as well as the typical behavior of owners in relation to similar land plot (purchase or lease).
7. In the absence of documented property rights of third parties in relation to the property being assessed, restrictions (encumbrances), as well as environmental pollution, the assessment of the object is carried out based on the assumption of the absence of such rights, restrictions (encumbrances) and pollution, taking into account the circumstances identified during the inspection , unless otherwise specified in the assessment assignment.
IV. Assessment task
8. The assignment for the assessment of a property must contain the following additional information to that specified in paragraph 17 of FSO No. 1:
• composition of the object of assessment, indicating information sufficient to identify each of its parts (if available); • characteristics of the appraised object and its appraised parts or links to documents available to the appraiser containing such characteristics; • rights taken into account when assessing the subject of assessment, restrictions (encumbrances) of these rights, including in relation to each part of the subject of assessment.
9. The assessment assignment may indicate other calculated values, including:
• market rent (the estimated amount of money for which a property could be rented at the valuation date under typical market conditions); • costs of creation (reproduction or replacement) of capital construction projects; • losses (actual damage, lost profits) upon alienation of a property, as well as in other cases; • costs of eliminating environmental pollution and (or) reclamation of a land plot.
V. Market analysis
10. To determine the value of real estate, the appraiser examines the market in those segments that include the actual use of the property being valued and other types of use necessary to determine its value.
11. Analysis of the real estate market is carried out in the following sequence:
a) analysis of the impact of the general political and socio-economic situation in the country and region where the property being assessed is located on the market of the property being assessed, including trends that have emerged in the market in the period preceding the date of assessment;
b) determination of the market segment to which the valued object belongs. If the real estate market is underdeveloped and there is insufficient data to provide an idea of the prices of transactions and (or) offers with comparable real estate objects, it is possible to expand the study area to territories that are similar in economic characteristics to the location of the property being evaluated; c) analysis of actual data on the prices of transactions and (or) offers with real estate objects from market segments to which the valued object can be classified under actual, as well as alternative options for its use, indicating the range of price values;
d) analysis of the main factors influencing the demand, supply and prices of comparable real estate, for example, rates of return, payback periods for investments in the real estate market, with intervals for the values of these factors;
e) main conclusions regarding the real estate market in the segments necessary to evaluate the property, for example, market dynamics, demand, supply, sales volume, market capacity, motivation of buyers and sellers, liquidity, price fluctuations in the market of the property being assessed and other conclusions. The scope of research is determined by the appraiser based on the principle of sufficiency.
VI. Best use analysis
12. Highest use analysis underlies estimates of the market value of real estate.
13. The most effective use is that use of real estate that maximizes its productivity (corresponds to its highest value) and which is physically possible, legally permitted (at the date of determination of the value of the property being assessed) and financially justified.
14. The most effective use of a real estate property may correspond to its actual use or involve other use, for example, repair (or reconstruction) of capital construction facilities existing on the land plot.
15. Analysis of the most effective use allows us to identify the most profitable use of the property, which market participants (buyers and sellers) focus on when setting the transaction price. When determining the market value, the appraiser is guided by the results of this analysis to select approaches and methods for valuing the property being appraised and selecting comparable real estate when applying each approach.
16. Analysis of the most effective use of the object being assessed is carried out, as a rule, based on space-planning and design solutions. For assessment objects, which include a land plot and capital construction objects, the most effective use is determined taking into account the existing capital construction objects. In this case, such an analysis is carried out by carrying out the necessary calculations or without them, if justifications are presented that do not require calculations.
17. An analysis of the most effective use of parts of a real estate property, for example built-in residential and non-residential premises, is carried out taking into account the actual use of other parts of this property.
18. An analysis of the most effective use of a part of a real estate property being reconstructed or subject to reconstruction is carried out taking into account the most effective use of the entire property being reconstructed.
19. The most effective use of a property valued individually may differ from its most effective use as part of the valued complex of real estate objects.
20. The market value of a land plot built up with capital construction projects, or capital construction projects for entering this value into the state real estate cadastre, is assessed based on the type of actual use of the property being valued. In this case, the developed land plot is assessed as undeveloped, intended for use in accordance with the type of its actual use.
21. An analysis of the most effective use of a real estate property for rent is carried out taking into account the conditions of use of this property established by the lease agreement or the draft of such an agreement.
VII. Approaches to assessment
22. When applying a comparative approach to real estate valuation, the appraiser takes into account the following provisions:
a) a comparative approach is used to evaluate real estate, when it is possible to select a sufficient number of analogous objects with known transaction and (or) offer prices for evaluation;
b) real estate objects that belong to the same market segment as the object being valued and are comparable to it in terms of pricing factors are used as analogue objects. At the same time, for all real estate objects, including the one being assessed, pricing for each of these factors must be uniform;
c) when conducting an assessment, the volume of market data available to the appraiser about similar objects and the rules for their selection for calculations must be described. The use in calculations of only part of the analogous objects available to the appraiser must be justified in the assessment report;
d) to perform calculations, specific indicators of value (comparison units) that are typical for a similar object, prevailing on the market of the object being valued, are used, in particular the price or rent per unit of area or unit of volume;
e) depending on the initial information available on the market, in the process of real estate valuation, qualitative valuation methods (relative comparative analysis, expert assessment method and other methods), quantitative valuation methods (regression analysis method, quantitative adjustment method and other methods), as well as their combinations.
When applying qualitative methods, real estate valuation is carried out by studying the relationships identified based on the analysis of transaction prices and (or) offers with similar objects or relevant information received from experts, and using these relationships to conduct an assessment in accordance with the technology of the method chosen for evaluation.
When applying the adjustment method, each analogue object is compared with the valued object according to price-forming factors (comparison elements), differences between objects are identified by these factors, and the price of the analogue object or its specific indicator is adjusted according to the identified differences in order to further determine the value of the valued object. In this case, the adjustment for each element of comparison is based on the principle of the contribution of this element to the cost of the object.
When applying regression analysis methods, the appraiser, using data from the market segment of the object being valued, constructs a pricing model that corresponds to the market for this object, from which he determines the estimated value of the sought value;
f) to compare the valuation object with other real estate objects with which transactions have been made or which are presented on the market for their completion, the following elements of comparison are usually used:
• transferred property rights, restrictions (encumbrances) on these rights; • terms of financing of a completed or proposed transaction (type of payment, credit conditions, other conditions); • terms of sale (conditions atypical for the market, transaction between affiliates, other conditions); • market conditions (price changes for the period between the transaction and valuation dates, discounts to offer prices, other conditions); • type of use and (or) zoning; • location of the object; • physical characteristics of the object, including the properties of the land plot, the condition of capital construction objects, the ratio of the area of the land plot and its built-up area, other characteristics; • economic characteristics (level of operating expenses, lease terms, composition of tenants, other characteristics); • availability of movable property not related to real estate; • other characteristics (elements) affecting the cost;
g) in addition to cost, the comparative approach can be used to determine other estimates, such as rental rates, depreciation and obsolescence, capitalization rates and discount rates.
23. When applying the income approach, the appraiser takes into account the following provisions:
a) the income approach is used to value real estate that generates or is capable of generating income streams;
b) within the framework of the income approach, the value of real estate can be determined by the direct capitalization method, the discounted cash flow method or the capitalization method using calculation models;
c) the direct capitalization method is used to evaluate real estate assets that do not require significant capital investments in their repair or reconstruction, the actual use of which corresponds to their most effective use. Determining the value of real estate objects using this method is carried out by dividing the annual income from the object corresponding to the market by the total capitalization rate, which is determined based on the analysis of market data on the ratio of income and prices of real estate objects similar to the object being valued;
d) the discounted cash flow method is used to evaluate real estate that generates or is capable of generating income streams with arbitrary dynamics of their changes over time by discounting them at a rate corresponding to the return on investment in similar real estate;
e) the capitalization method based on calculation models is used to evaluate real estate that generates regular income streams with the expected dynamics of their change. Capitalization of such income is carried out at a general capitalization rate, constructed on the basis of the discount rate taken into account in the calculation of the capital return model, methods and conditions of financing, as well as expected changes in income and property value in the future;
f) the structure (taking into account taxes, return of capital, rate of change in income and asset value) of the discount rates and (or) capitalization used must correspond to the structure of the discounted (capitalized) income;
g) for real estate that can be rented out, rental payments should be considered as a source of income;
h) the valuation of real estate intended for running a certain type of business (for example, hotels, restaurants, gas stations) can be carried out on the basis of information about the operating activities of this business by separating from its value components that are not related to the real estate being valued.
24. When applying the cost approach, the appraiser takes into account the following provisions:
a) the cost approach is recommended to be used for the valuation of real estate - land plots built up with capital construction projects, or capital construction projects, but not their parts, for example, residential and non-residential premises;
b) it is advisable to use the cost approach to evaluate real estate if it corresponds to the most efficient use of the land plot as undeveloped and it is possible to correctly assess physical wear and tear, as well as functional and external (economic) obsolescence of capital construction projects;
c) the cost approach is recommended to be used when market activity is low, when there is insufficient data necessary to apply the comparative and income approaches to valuation, as well as to evaluate real estate for special purposes and uses (for example, linear objects, hydraulic structures, water towers, pumping stations, boiler houses , utility networks and other real estate for which there are no market data on transactions and offers);
d) in general, the value of a property, determined using the cost approach, is calculated in the following sequence: • determining the value of rights to a land plot as undeveloped; • calculation of costs for the creation (reproduction or replacement) of capital construction projects; • determination of the entrepreneur's profit; • determination of wear and tear and obsolescence; • determining the cost of capital construction projects by summing up the costs of creating these facilities and the entrepreneur’s profit and subtracting their physical wear and tear and obsolescence; • determining the value of a real estate property as the sum of the value of rights to a land plot and the cost of capital construction projects;
e) for the purpose of determining the market value of a property using the cost approach, the land plot is assessed as undeveloped, assuming its most effective use;
f) calculation of costs for the creation of capital construction projects is carried out on the basis of: • data on construction contracts (agreements) for the construction of similar objects; • data on the costs of construction of similar facilities from specialized directories; • cost estimates; • information on market prices for building materials; • other data;
g) the costs of creating capital construction projects are defined as the sum of the costs included in the construction and installation work directly related to the creation of these objects, and the costs associated with their creation, but not included in the construction and installation work;
h) for the purpose of assessing the market value of real estate, the amount of profit of an entrepreneur is determined on the basis of market information using extraction methods, expert assessments or analytical models, taking into account direct, indirect and opportunity costs associated with the creation of capital construction projects and the acquisition of rights to a land plot;
i) the amount of wear and tear and obsolescence is defined as the loss of real estate value as a result of physical wear and tear, functional and external (economic) obsolescence. At the same time, wear and tear and obsolescence relate to capital construction projects related to the real estate being assessed.
25. The appraiser has the right to use a different calculation methodology and independently determine the method (methods) of real estate valuation within each of the selected approaches, based on the principles of materiality, validity, unambiguity, verifiability and sufficiency. In this case, the assessment report must provide a description of the method(s) chosen by the appraiser, allowing the user of the assessment report to understand the logic of the process of determining the value and the compliance of the method(s) chosen by the appraiser with the property, the principles of assessment, the type of value being determined and the intended use of the assessment results.
VIII. Coordination of assessment results
26. Coordination of real estate assessment results obtained using various methods and approaches to assessment, and reflection of its results in the assessment report, is carried out in accordance with the requirements of FSO No. 1 and FSO No. 3.
27. If several valuation methods are used within any approach to real estate valuation, preliminary approval of their results is carried out in order to obtain an intermediate result of real estate valuation using this approach.
28. In the process of coordinating the intermediate results of real estate valuation obtained using different approaches, it is necessary to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of these approaches, explain the discrepancy between the intermediate results and, based on the analysis, determine the final result of the real estate valuation.
29. If there is insufficient market data necessary to implement any of the approaches to real estate valuation in accordance with the requirements of this Federal Valuation Standard and FSO No. 1, FSO No. 2, FSO No. 3, within the framework of the chosen approach based on the available data, it is recommended to indicate indicative values (value) of the value being assessed, which are not taken into account in the final approval, but can be used as verification for the final result of the real estate assessment.
30. After the approval procedure, the appraiser, in addition to indicating in the assessment report the final result of the assessment of the value of real estate, gives his judgment on the possible boundaries of the interval in which, in his opinion, this value may be located, unless otherwise indicated in the assessment task.
Is it possible to conduct an assessment in the future?
It is impossible to evaluate an object at a date in the future. No one can know for sure how the property will improve or deteriorate in a year, two, ten years, etc. In addition, completely unexpected things can happen. For example, a fire or hurricane that destroys the object or most of it.
By the way, at the beginning of 2020, everyone was making “standard” forecasts for the relative current year. No one could predict the appearance of a black swan
— the coronavirus pandemic, which is having a devastating impact on the entire global economy. As of this writing, we are still in crisis. Who can predict when the self-isolation regime will end, when the economy will begin to recover, what growth rates it will have? But this affects the value of all assets.
However, the appraiser can determine the potential profit that the property could generate if used in the future. For this purpose, the income approach is used. It is based on forecasting and using estimated data for the future period. But such a service will be more of a consulting nature.
Cost of professional assessment
How much does the assessment procedure cost? Typically, the cost of appraising an apartment varies between 2-5 thousand rubles . It depends on the following factors:
- location of the property and the appraising organization;
- qualification of the appraiser;
- area and other characteristics of the apartment.
An apartment appraisal report for a notary is issued for a period of six months, since it is during this period that it is necessary to enter into an inheritance . The certificate for the court is unlimited, since it certifies the cost of housing precisely at the time of the death of the testator, and only this factor is important for the judge.
A professional appraisal of an apartment is not included in the main stages of inheritance. However, it is unlikely that it will be possible to do without this procedure.
There should not be any particular difficulties with the assessment if you contact qualified appraisers who are members of the SRO and strictly follow the other recommendations from this article.
Documentation
Documents for the company and appraisers are attached to the Valuation Report:
- Insurance policy for the company;
- Diploma of education, Advanced training;
- Certificate of membership in the SRO, Extract from the SRO register;
- Insurance policy for the appraiser.
Mandatory requirements are the relevance of documents as of the date of preparation of the Report: we are talking about both documents of appraisers and documents on the object of assessment. By the way, the date of issue of documents for the assessment object cannot be later than the date of assessment, much less the date of preparation of the Report.
But can the appraiser carry out a retrospective assessment when he may not have had a diploma yet? Yes maybe. For example, an assessment is required for 2012, but a specialist only became a full-fledged appraiser in 2020. In the appraisal industry, as in any other, there is a natural rotation of specialists and their transition to other areas. And for example, a client needs to evaluate shares for 2012 for a notary. Why not?
Falsification.
Some appraisal companies abuse their capabilities and issue false Reports.
For example, when the Report was supposed to be in the court case a year ago, but in fact the document is released today, but retroactively. The report is not in the register on the SRO website and is illegitimate. You can read more about checking appraisers and Reports in the corresponding article on the website.
Let us summarize the above once again: the inspection of the object should be carried out exactly as of the date of assessment. Documents attached to the Report and dated after the valuation date are unacceptable.
Updating the Report
There is a popular service that has recently been used less and less by our clients - updating the assessment report. Most often, banks needed this service. But several years ago, banks switched to independently assessing all collateral. Before this, there was a different practice - the appraisal company had to annually re-evaluate the collateral and issue an updated report to the client.
When updated, the Report template is already ready. So what is the job of an appraiser?
- It is imperative to inspect the object being assessed. In practice, there were cases when the client forgot that changes had occurred at the facility during the year: for example, they purchased additional equipment items or, on the contrary, wrote them off, put into operation an extension to the building, or demarcated the site. Such situations often occur in practice.
- Conduct a market analysis. Right now the market is dead in most sectors. Nothing much changes anywhere. But, changes in external factors may occur: it is planned to build a metro station, or open a new interchange, or the permitted type of use of the site has been changed based on the master plan for the development of the territory.
- Carry out a new calculation. Based on the updated conditions, it is necessary to make a new calculation. Even in a dead market, information changes and is updated.
- Prepare an updated Report. Of course, the report template has already been filled out. But the appraiser also needs to spend time updating all the information.
An example from life.
The client carried out an appraisal of the property in one appraisal company. Now he needed to update the old Report, but he was not satisfied with the price for the work of that company. Addressing us, before we made him an offer, he says - I only need to update the Report, and not make a new one. But we need to make a report from scratch, because we are not yet familiar with this object.
Documents required for real estate valuation
- Title documents for real estate
- Real estate documents reflecting quantitative, qualitative, technical characteristics.
- Information about the Customer of the assessment:
- for legal entities: organizational and legal form; full name; main state registration number (OGRN), date of assignment of OGRN; location;
- for individuals: Full name Customer; contact number; series and number of the identity document, date of issue and authority that issued the document.
List of documents for real estate assessment
is preliminary in nature and can be shortened or expanded after the appraiser has thoroughly familiarized himself with the object of assessment and the purposes of the assessment.
Documents for real estate valuation
are provided in a way convenient for you based on agreement with the appraiser.
On what date can a business be valued?
The need to evaluate a business arises in various cases, for example, during its sale or reorganization, issuing secured loans, or an issue. The Valuation Report must indicate the valuation date, which is determined by:
- the date of preparation of the last annual financial statements, if no more than 6 months have passed since their preparation;
- date of interim reporting (optional). And if there are no financial statements or significant changes have occurred since their preparation, then it is necessary to request up-to-date data from the company.
Once again, annual financial statements are the most reliable, since they are mandatory and submitted to the Federal Tax Service. All counterparty verification services are based on this data. Due to the fact that a business is a “living organism”, the valuation date should be as close as possible to the date of preparation of the Reports.
What property is subject to valuation?
The inheritance may include movable and immovable property. The following types of property are subject to assessment:
- private houses.
- apartments in an apartment building.
- land.
- shares in the authorized capital of an economic entity.
- enterprise securities.
- property complexes.
- industrial equipment.
- weapon.
When is an assessment required?
When entering into an inheritance, an assessment is required in the following cases:
- when submitting documents to a notary;
- when submitting documents to the court to establish the fact of acceptance of the inheritance in court;
- in case of litigation with other heirs.
Let's consider whether it is possible to do without an assessment. Citizens exempt from paying fees may not order assessment documents. However, this option is possible if the person entitled to the benefit is the only heir.
In addition, citizens who inherit:
- residential premises in which they lived together with the testator;
- funds on deposits.
It is worth considering separately whether a report is needed when actually accepting an inheritance. The possibility of exemption from paying the duty is provided depending on the identity of the heir or the type of property. The method of accepting the inheritance does not matter. When registering property, the actual heirs undergo a full list of procedures, including assessment (Article 1153 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Be sure to read it! Statement on establishing a fact of legal significance: sample and procedure for execution
The only difference is that the heir contacts the notary at any time. The assessment must be made in advance.
What is the validity period of the peer review report?
The appraiser must indicate this validity period in his report.
Valuation of property for court
As for conducting an expert assessment of property for the purpose of presentation in court, there is no clear answer to the question about the validity period. On the one hand, the established practice is that the market value determined by the appraiser, by analogy with the valuation for a notary, is valid for six months. However, the final decision is the prerogative of the judge and may depend, in particular, on whether there have been significant changes in market conditions or fluctuations in exchange rates over the past months. National Standard No. 1 states that if there are no clear legal requirements for the validity period of the report in a particular case, it is accepted at the discretion of the assessment user.
Valuation of communal property for rent
Here, too, there are some peculiarities related to the fact that the review (that is, checking the correctness) of reports by the Department of Municipal Property of Kyiv in some cases drags on for several months. Despite the fact that internal regulations of the Department sometimes change the validity period of assessments from six months to a year, we recommend submitting documents there without delay. As is known, the determination of the value of communal property is carried out on the last day of the month. That is, if the documents were made as of May 31, in order for the procedure to go through without unnecessary problems, the package must be submitted during June.
Other assessment cases
If you are not satisfied with the answer to the question about the validity period of the expert assessment report (your case is not described or the answer is not sufficiently legally justified), we advise you to additionally read an article on a similar topic on the website of the All-Ukrainian public organization “Association of Appraisal Specialists”. We also recommend watching a video about what a real estate valuation report is and looks like.
5. Determining the value of the object
The determination of value is carried out taking into account all factors that significantly influence both the real estate market as a whole and directly the value of the property in question. When determining the value of real estate, three main methods are usually used:
— costly method;
— method of direct comparative analysis of sales;
— income capitalization method.
Using three methods results in three different values for the same object. After analyzing the results obtained by different methods, the final assessment of the value of the property is established based on which method(s) is most suitable for the property being valued.
5.1 Cost method of valuation
The main steps in applying this approach to determining cost are:
1) Determine the value of the land plot in the proposal that it is not developed;
Cost of land plot (without buildings) = 62m 2 x 1.77 x 1.5 x 3,230 rub.
. x 1.2387 = 658,604 rub.
Cost of land acquisition for development = S zu*384
rub./sq.m = 62 m2 x 384 rub. = 23 808
2) Determine the replacement cost of improvements (buildings, structures, improvement objects) located on the land plot;
Replacement cost of the building = C69*Os*Km*K84*Kp*Kz*Knds
BC=186x28.3x1.02x1.17x107.62x1.3x1.18 =1,037,059, 71 rub.
3) Determine the amount of accumulated wear (1681126);
Total cost = 4,437,658 rubles.
Market value (including transfer to non-residential stock) = 4,437,658 * 1.45 = 6,434,603 rubles.
When assessing an office, we do not take into account functional wear and tear, since this object meets all technical and functional requirements and has a typical layout for office premises. External wear and tear is also not taken into account, since the office has a favorable location, that is, there is a parking lot nearby and there is convenient access to the office.
5.2 Comparative method
In order for the objects to be comparable, we will take objects from the same economic zone of the city and the most closely adjacent buildings.
Market price = 8,122,000
5.3 Income method
1. The value of real estate is assessed as the current value of future cash flows, i.e. reflects:
- the quality and quantity of income that the property can bring during its service life;
— risks specific to both the object being assessed and the region.
2. Used in determining the investment and market values of an object.
The income capitalization method is to obtain the present value of future benefits from owning real estate.
1) Calculate net operating income (NOI):
NRR = average rental rate per year * S of the building
CHOD = 1090 rubles * 12 * 62 sq.m.