Home / Family law / Inheritance
Back
Published: 08/05/2018
Reading time: 5 min
0
189
In Russia, the custom of writing a will is not common; most often, in the event of the death of one of the family members, inheritance occurs according to law.
- Who is the first priority heir?
- Procedure for entering into inheritance
According to the third part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, heirs of the first priority are called upon to inherit according to the law.
Inheritance of property by will
The transfer of property by will is carried out if, at the time of the citizen’s death, there is a valid order regarding his will regarding who should receive his property: apartments, cars and other assets. At the same time, it is important that none of the relatives have any doubts that the will was drawn up personally by a deceased relative, for example, a father, and at the time of its execution he was in full legal capacity, that is, he was aware of his actions and their possible consequences. Otherwise, this document may be contested, which means that the entire procedure for distributing property in accordance with it will be declared invalid. If there is a will, in accordance with the law, the order prescribed in it takes precedence: all assets belonging to the deceased must be distributed exactly as he wished. For example, an apartment may be left by a father in his will to one of his sons, despite the fact that he has other children. The only exception may be a situation where the father did not mention minor or disabled children, parents, dependents or a spouse: in this case, in this part the law requires that the last will of the deceased be violated by providing such relatives with a part of his property in the amount of at least half of that amount , which they would have received if the will had not existed.
Transfer of property of a deceased person by law
If there is no order from the owner regarding the distribution of his property at the time of death, the mechanism described in the law should be used. In particular, Article 1141 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides that in such a situation, inheritance is carried out in accordance with the relatives’ belonging to the so-called queues. Their composition is determined on the basis of the relationship between the deceased and his relatives, which can be based on kinship, property or dependency. For example, the first priority includes children, parents, and a spouse of a citizen. The second line is formed by his grandmothers, grandfathers, brothers and sisters, including both full and half-blooded ones, that is, having only a common father or mother with him. Inheritance of property, in accordance with the legal order, provides for the priority of each previous order in relation to the next. So, for example, if there is at least one heir of the first stage, representatives of all subsequent stages do not have the right to receive property. Thus, for example, if at the time of the death of a citizen he no longer has parents and a spouse, and the only heirs of the first priority are his two children, they will receive all of his property, regardless of whether there are applicants in other queues and what their number is.
The right to inheritance by law: a brief description
Relatives receive this right after the death of the testator or its official recognition in court. This circumstance must be confirmed by a death certificate.
Second-rank applicants can also receive rights to inheritance if the first-priority relatives renounced their legal right to the welfare of the deceased for one reason or another.
In order to receive property without a will, you must first make sure that the will as such has not been drawn up and certified by a notary.
In principle, any notary can provide such information, since all wills are stored in a special database to which they have access.
Order of heirs
The order of heirs is determined by blood or marriage. Below is the order of succession of heirs, drawn up in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation:
- Spouses, children and parents who have not renounced the inheritance.
- Oddly enough, brothers or sisters are not included in the first category; they form the second, along with grandparents, as well as nephews, in the event of the death of their parents, who inherit property by right of representation.
- Uncles, aunts, cousins.
- Great-grandparents.
- Children of nephews and nieces.
- All cousins.
- Non-blood parents who had parenting rights.
This list can be supplemented with information that in the case where there are no heirs, the property is considered escheated and becomes the property of the state, represented by local government bodies - the administration. Thus, you should not delay the registration, as there is a possibility of being left with nothing.
Entry into inheritance rights: contacting a notary
In order to enter into your rights, in both cases: when inheriting by law, and when receiving property under a will, you must contact a notary.
The applicant must write a statement in which he records the fact of taking over his rights and asks to issue a certificate of the right to inheritance, for example, for an apartment left to his son after the death of his father. Such an application must be accompanied by documents confirming the validity of such claims on the part of the applicant. This package must include the applicant’s passport, death certificate of a relative, and a certificate from his place of residence confirming his address of residence and permanent registration. In addition, depending on whether property is distributed according to a will or by law, the package of documents should be supplemented with other papers. So, if there is a valid order of the deceased regarding the procedure for dividing his property, the notary must be familiarized with it, proving, for example, the validity of the son’s claims to his father’s apartment. If the division of assets occurs in accordance with the legal order, the applicant must confirm the legitimacy of his claims by providing evidence of his membership in a certain line of inheritance. The easiest way to do this is for representatives of the first line: for example, the parents of the deceased will only need to provide a certificate of his birth, the children - a certificate of their birth, and the spouse - a marriage certificate. The applicant must submit documents to a notary, thereby declaring his rights to receive the property of a deceased citizen, within a period not exceeding six months from the date of his death or from the day he was declared dead. If this deadline has been missed, acceptance of the property, including an apartment, is possible, but to do this you will have to go to court, presenting evidence of valid reasons why the applicant failed to meet the deadline allotted by law. If the judicial authorities recognize the sufficiency of these grounds, the period for accepting the property will be restored. Having received the necessary documents, the notary will open a so-called inheritance case. After this, he will study all his circumstances, including the composition of the property that should pass from the deceased owner to his relatives, the presence of other heirs and the grounds for their rights to receive property, including applicants for the acquisition of compulsory shares. It will analyze the legitimacy of the documents submitted by the applicant or applicants and make a determination as to whether his or their claim to receive the deceased's property, including the apartment, is valid. If he recognizes them as such, within the period prescribed by law, the notary will issue the applicant with a certificate of right to inheritance.
This certificate is a key document confirming the rights of a relative of a deceased citizen to acquire his assets. Subsequently, he will be able to apply with this document to the state registration authorities. On this basis, they will be able to record his rights to this property and issue a certificate of ownership, which gives him the opportunity to dispose of this property and use it at his own discretion. It is important to remember that it will be possible to obtain a certificate of inheritance no earlier than after the expiration of the period allotted by law for its adoption, regardless of the date of filing the documents. Thus, the applicant will be able to become the owner of this certificate only six months from the date of the death of his relative, for example, his father, or he was declared dead. This restriction is established by law so that all applicants who have the right to receive his property have time to contact the relevant authorities, stating their claims.
Who inherits after the death of their father?
- Documentation
- If the father disinherited
The order of inheritance varies depending on the basis. Art. 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes the following grounds:
- in law;
- by will;
- under an inheritance agreement.
Without a will
In case of inheritance without a will after the death of the father, the following have the right to a share in the inheritance:
- Official wife. If at the time of death the father was cohabiting with a woman, she has no right to inheritance. The only option for obtaining a share in property without a will from a common-law wife is recognition as a dependent of the deceased.
- Children. Children from all marriages, adopted children, as well as those for whom paternity was established voluntarily or through the court have the right to the property of the deceased father. They all have equal rights to inheritance.
- Parents. If the mother or father is alive, they are also entitled to a share in the property.
- Dependents. Together with the heirs of the first stage, the disabled dependents of the deceased enter into rights. These are relatives or strangers who were supported by the deceased for at least 1 year. If an outsider claims the right to a share, he must prove that he lived with the testator for at least 1 year and ran a joint household.
By will
According to the will, the father can assign his property to relatives, strangers, enterprises and the state. But freedom of expression is limited by the right to an obligatory share.
Art. 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the obligation of the testator to provide for minor children, disabled parents, spouse and dependents a share in the property. It should not be less than ½ of the inheritance that would be due to them by law.
If the will does not provide for a part for compulsory heirs, then the successor may challenge the document in court. In this case, the share is allocated, proportionally reducing the shares of the heirs under the will.
I would like to additionally note inheritance by testamentary disposition. A testamentary disposition is a document that provides for the procedure for transferring rights to a bank account in the event of the death of the depositor. That is, any investor can bequeath their savings completely free of charge. To do this, you do not need to contact a notary. The document can be issued directly at the credit institution.
If the father dies, the heirs need to check whether he had bank accounts.
Since 2020, the notary independently receives information from Sberbank. But you will have to make notary requests to other credit institutions.
An inheritance agreement is concluded between the testator and any of the heirs. The document includes the procedure for the heir's actions in the event of the death of the owner. The owner of the property has the right to determine by agreement any circle of heirs, including children or not.
Take the survey and a lawyer will share an inheritance action plan in your case for free
Entry into inheritance rights: actual acceptance of inheritance
In addition, it is necessary to take into account that the law allows for the possibility of dispensing with the formal legal procedure for registering an inheritance and contacting a notary. Thus, Article 1153 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the acceptance of property also recognizes the actual assumption of property rights by a relative of the deceased. In order to carry out such actual entry, the latter must take one of the actions indicating his intentions. As such actions, the law provides for the beginning of ownership, use or management of the property of the deceased, its protection from attacks on it by other persons who do not have the right to it, or other measures to preserve such property, for example, you can cover the car with a cover or put it in the garage . Among such actions, the law includes payment by a relative of expenses necessary to maintain the property of the deceased in proper condition, for example, payment of utilities for an apartment. In addition, this includes the payment of debt obligations of a deceased relative or, conversely, the receipt of funds that were due to him from debtors.
Article 1153 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the documentary method of entering into inheritance rights by applying to a notary and the actual entry into inheritance are equally legitimate ways of acquiring the property of a deceased relative, for example, a father. It should, however, be remembered that in order to ensure the full scope of their rights to dispose and own their property, for example, to sell an inherited apartment, the new owner will need a certificate of ownership. In this case, he will still have to apply first to a notary for a certificate of inheritance, and then to the state registration authorities to obtain a certificate of ownership. However, in this situation, he can inherit it regardless of the period of application: he cannot be charged with missing the deadline for accepting the inheritance, since he actually accepted it.
Chapter
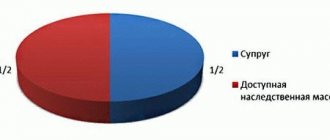
After the death of the mother, father or spouse, the inheritance begins to be divided by the successors from the first line. In the first case, the inheritance is distributed according to established norms, but if one of the spouses dies, then the status of the property is also subject to consideration. That part of it that was acquired during the marriage is divided in half. In this case, ½ is not property that is subject to division between relatives from the first line, but a part of the second spouse, since it was acquired during the marriage.
The second half is the legal share belonging to the testator. It belongs in equal shares to the parents, children, and the remaining spouse. In the same case, when the property was acquired before marriage or a person owned it based on the fact of a gift, it is divided among all heirs in equal parts. Entry into the inheritance must take place within six months from the date of death of the person - the notary must provide the relevant documents. If the papers are not submitted, then at the legislative level this can be regarded as a refusal to inherit the due part of the property; the degree of relationship is not the main factor here.
Thus, the order of inheritance, as well as the peculiarities of this process, are clearly and clearly stated in the current acts and laws. Compliance with the rules ensures that all people who are heirs receive their share of the property.




![eCabbage [CPL] RU](https://standart-rzn.ru/wp-content/uploads/ekapusta-cpl-ru-330x140.jpg)