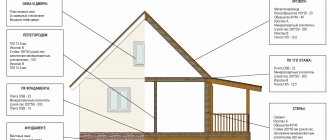
The building area is the occupied area of land for the finished building. Its value is determined by the horizontal projection of the object onto the foundation plane. This term is used to refer to the cross-sectional area of the entire house in the horizontal plane.
In this case, a visual section is drawn along the base, taking into account all protruding parts. For example, it is considered that a porch, terrace, veranda, gallery, ramp are included in the building area of the house, but protruding parts of a balcony or roof are not, unless they are supported by load-bearing supporting pillars.
Construction area of a residential building
This value is calculated after finishing work is completed. The built-up area of the room includes the floor area (plinths are not taken into account). If there is a stove or fireplace, their dimensions are not included in the footage. To calculate the building area of a balcony or terrace, only the internal contours are taken without taking into account the fences.
Many homeowners are interested in how to calculate the total built-up area of a residential building. To do this, you need to sum up the values of all rooms. In addition to residential premises, the calculations also include the areas of the following auxiliary areas:
- Built-in wardrobes.
- Loggias.
- Verandas.
- Storerooms.
- Tambours.
There is a distinction between living and useful space. What is the built-up area of living space? This is the total size of all residential premises located in the building. Only rooms with ceilings with a height of at least 2.2 m are subject to registration.
The intended purpose of such premises is for permanent residence. The usable area is not an area intended for living. This includes auxiliary areas located within a residential building.
To find the total built-up area of a residential building, you need to sum up the dimensions of residential and auxiliary premises.
If the structure is placed on supports, the entire space located under the structure is counted in the footage.
For summer cottages and gardening non-profit partnerships (SNT) with dimensions of 0.06 - 0.12 hectares, the following standards apply: the building area allocated for the construction of houses, as well as the arrangement of paths, platforms and other objects in total should not exceed 30% of the total available building area of the land plot.
What is the built-up area? Design and construction
If the size of a dacha or garden plot does not exceed 0.06-0.12 hectares, then the space occupied by buildings, paths, blind areas, platforms and existing hard surfaces should not occupy more than 30% of its entire territory. As a rule, in individual housing construction, data from local regulatory frameworks are used. Sometimes they may be unavailable or simply not exist.
There is also the concept of building density coefficient. With its help you can estimate the possible volume of the building. It is equal to the ratio of the total area of all floors (both above-ground and basement) to the size of the site. Moreover, the external dimensions of the building are taken into account.
Regulations
In order to independently determine the footage of buildings and the area of the building, the homeowner needs to study the current state norms and rules. All requirements are set out in detail in a document called “Building Standards and Rules” (SNiP).
It also contains a detailed description of residential buildings and a list of applications that need to be used when designing and constructing buildings. This document regulates methods for measuring the dimensions of residential and auxiliary premises between walls, ceilings and other partitions.
How to determine the area of open spaces - balconies, loggias, terraces, etc.? To fix their dimensions, measurements are taken along the internal contours between the walls and fences.
House area: total, built-up area and others
Good evening! I live in Krymsk, a little unlucky, my house was flooded. Yesterday I had a commission working, and so this is what they don’t want to pay for - in fact, there is, but it’s not reflected in the BTI plan. I say: “But you see that it actually exists, and it is in the description.” Answer: “So what? But it’s not on the diagram” 2-An interesting play on words: in the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated July 17, 2012 No. 1015 p 3. “…. provide for the allocation of funds for major repairs of damaged housing in settlements affected by floods, based on the cost of repairing one square meter of housing 5 thousand rubles (the total amount is allocated for one household or apartment). Determine the procedure for allocating these funds.” :The Governor of the Krasnodar Territory dated July 20, 2012 No. 830 1. .....for major repairs of damaged residential premises, based on the cost of repairing one square meter of damaged housing 5 (five) thousand rubles (the total amount is allocated for one residential premises, flood damaged). What is the difference? But here’s the thing, Alexander Nikolaevich, in his resolution there is the phrase “DAMAGED RESIDENTIAL PREMISES”, and because of these three words, social protection refuses to pay for repairs. In fact, I have housing on different levels, for example, if the room indicated on the diagram as the kitchen was flooded (although this is actually a living room, and they see it.) then it is not RESIDENTIAL (!) and there is no NEED to allocate money for its repair! And there’s no point in talking about a garage that has a common wall with the house and stands on the same foundation. Other buildings that are not “in contact” with the house are not even considered. It turns out that in every building there is an area that always remains dry - this is the area of the walls. For example, if the outer perimeter of the building is 10 x 10 meters, and it is all in water, then this is not 100 square meters flooded! When calculating, they will only calculate the internal area of the rooms, the difference in area will be tens of meters. A simple and understandable word in the Presidential Decree is “housing,” but it turns out that different commissions interpret it differently. For my family, such a difference in the understanding of the word housing results in an amount of more than 400,000 rubles! They say that if your Decree had written “damaged households,” then it would be a completely different matter. In fact, this is all mixed up in an ordinary play on words and concepts. .How to correctly calculate the flood area, link to the law.Thank you!
See above: Notes, order No. 531, which does not contradict SNiPs and federal law. The veranda (glazed) and cold storage room are summed up in the total area with a coefficient of 1.0 (that is, they are fully taken into account, unlike loggias, balconies and open terraces). The closet on your floor is your total area, the staircase must be counted as the room in which it is located (only once), BUT. if you actually own part of the first floor on which the staircase is located, this room will also be part of your apartment. Sincerely, EI PS If you do not agree with the measurements, you demand in writing to provide you with the local regulatory framework on the basis of which the plan was made for you, then, in accordance with this document, you demand in writing to correct what does not correspond, then in case of a written refusal you contact court.
Features of calculating the building area of multi-storey buildings
The number of floors of a house also has a certain meaning in calculations. An above-ground floor is considered to be a level with the top of the floors located above two meters. Underground and interfloor spaces below 1.8 meters are not considered above-ground floors.
If a building consists of several parts with different numbers of floors or is located on a sloping area, which necessitates the construction of several floors, all its parts are calculated separately.
Multi-storey apartment buildings also have their own characteristics. The total area is determined here using reduction factors:
- for terraces and balconies - 0.3;
- for a loggia - 0.5.
Multi-level apartments, as a rule, are equipped with inter-apartment staircases. If the height of the march is more than 1.6 meters, its footage must also be taken into account.
The dimensions of a residential building are determined by summing up the data obtained from measurements on each floor. The results of measurements taken on the balconies, loggias and staircases that are part of the house are also added here.
Tip 1: How to calculate the building area
1. According to the building codes and regulations in force on the territory of the Russian Federation - SNiPs, and, in particular, SNiP 31-01-2003 “Residential multi-apartment buildings”, the building area is set equal to the horizontal section area along the external silhouette of the building on the plinth tier. At the same time, it takes into account all the protruding parts of the building with ceilings - balconies, terraces, galleries, verandas and porticos. If there are architectural details of a building supported on poles, then they are also included in the total building area .
When a person is faced with the issue of selling or buying an apartment, he needs to have an idea of its parameters and considerations. One of the main such parameters is the area of the apartment, and not the primitive area, but the one that is universal and the one that is considered residential. They will never be equal and the general area is invariably larger than the residential area. Even without seeing the apartment, based on these two parameters you can already form a first impression about it. Consequently, they are often indicated in the description of apartments put up for sale.
Building density indicator
The density of the built-up area is determined in accordance with the requirements and recommendations of building codes and regulations in force in domestic legislation. General recommendations are reflected in federal documents.
However, each region has also developed local rules that take into account construction and its features in specific localities. The principles and rules of calculation in these regions often differ from each other for legal reasons.
For example, in the Moscow region, where the highest population density is observed, the building density ratio is 40%. These data are twice as high as those recommended by general federal rules, which provide for the development of urban land areas with a coefficient of 20%. Local administrative authorities are allowed to adjust this indicator.
The development coefficient is equal to the ratio of the area occupied by construction projects to the size of the entire land plot. In other words, you need to divide the building area into the total dimensions of the territory.
Using the building density coefficient, suitable design options for new buildings and their number of floors are selected. The most acceptable areas of premises are determined in accordance with the size of land plots.
CLARIFICATION OF THE AREA OF THE LAND
B. UTKIN Boris Utkin, head of the land rights registration department of the Moscow Regional Registration Chamber. The most important characteristic The problem of clarifying the area of a land plot arose already at the very initial stage of land reforms in Russia (in 1990 - 1992), when rules on land ownership, the possibility of buying and selling land plots, etc. appeared in the legislation. But this is especially relevant the topic became after the entry into force of the Federal Law “On State Registration of Rights to Real Estate and Transactions with It” dated July 21, 1997 Federal Law N 122-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law N 122). The fact is that justice institutions, in the process of conducting a legal examination of documents applied for registration, began to compare the area values indicated on the plan of the land plot with the data of the title document. The area of a land plot is one of its most important characteristics as a real estate property. The area is the basis for determining the cost indicators of a land plot; it must correspond to the minimum and maximum sizes established by law for a particular type of permitted use of a land plot, etc. From the standpoint of cadastral registration, the basis for identifying a land plot is the coordinates of turning points on the Earth’s surface. From a legal point of view, the most important thing is accurate information about what size part of the earth’s surface the claimant claims and whether he has grounds for this. With the adoption of Federal Law No. 28-FZ of January 2, 2000 “On the State Land Cadastre,” when land managers began to work closely on surveying previously allocated land plots, discrepancies between the data of title documents and cadastral plans began to occur en masse. For example, the certificate of inheritance shows 6 acres (as indicated in the testator’s documents), and on the new plan the area of the plot is 8 acres. Or, on the contrary, according to an act of a local government body, a citizen was given ownership of 12 acres, but only 10 acres are indicated on the plan. Since the cadastral plan is a mandatory appendix to the title document submitted for the state registration of rights (clause 1 of Article 17 of Federal Law No. 122), then if there is a discrepancy between the areas on the plan and in the document, the institution of justice for the state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it has the right to believe that the plan presented is not the one for which rights are being claimed, and to refuse registration. This raises the following questions: 1) to what extent is it possible that there may be a discrepancy between the areas of the land plot indicated in the title document and on the cadastral plan? 2) which body and within what limits can legally clarify the area of a land plot? Let's try to answer these questions. Confused law In the new edition of paragraph 4 of Art. 18 Federal Law No. 122, which entered into force on September 18, 2003, states: “Updated data on the boundaries and area of a land plot can be entered into the Unified State Register of Rights without re-registration on the basis of information provided by the body carrying out activities for maintaining the state land cadastre, if available consent in writing of the right holder (right holders) of the land plot or on the basis of an application from the right holder. If there is a dispute between the body carrying out the activities of maintaining the state land cadastre and the right holder, updated data on the boundaries and area of the land plot may be entered into the Unified State Register of Rights on the basis of a judicial act that has entered into legal force.” When read separately, this norm simply causes amazement: how can entries in the register be changed only on the basis of an application from the copyright holder, without any title document? What if he wants to “clarify” his six acres to the size of one hectare?! Meanwhile, everything is not so scary, since it is not individual norms that apply, but the entire Law as a whole. And in paragraph 8 of Art. 12 Federal Law No. 122 states that changes to entries in the Unified State Register of Rights that do not correspond to the title document are carried out in the manner established by Art. 21. Let us turn to this article, which reads: “In cases where there are grounds to believe that the correction of a technical error may cause harm or violate the legitimate interests of copyright holders or third parties who relied on the relevant registration records, such correction is made by decision of the court, arbitration court." Now the situation is becoming clearer. Since any increase in the area of a land plot at the expense of lands in state or municipal ownership always affects the interests of at least one third party, namely the Russian Federation (before the delimitation of state ownership of land), such clarification is possible only in court. But then, what are the limits for clarifying the area of a land plot on the basis of an application from the copyright holder or the body carrying out the activities of maintaining the state land cadastre, which is discussed in paragraph 4 of Art. 18 Federal Law No. 122? The answer to this question is contained in the Methodological Recommendations for conducting land surveying of land management objects, developed in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06/07/2002 N 396 and approved by Roszemkadastr on 02/17/2003. According to the specified document, the permissible discrepancy between the areas (delta Rdop) between the calculated area of the land plot and the area specified in the title document (Rdok) is calculated using the formula 1/2 delta Rdop = 3.5Mt X (Rdok), sq. m, where Mt is the mean square error of the position of the boundary sign, the value of which, depending on the category of land, varies from 0.1 (land of settlements (cities)) to 5.0 (land of the forest fund, land of the water fund, land of the reserve). Using the above formula, it can be calculated that for a land plot with an area of, for example, 1 hectare, located in a city, the permissible discrepancy between the areas on the plan and in the title document should not exceed plus/minus 35 square meters. m, and for the same area of the forest fund a discrepancy of plus/minus 1750 sq. m is allowed. m. It is within the specified limits (in this example) that it is possible to clarify the area of a land plot in the Unified State Register of Rights. But if the discrepancy between the areas is greater than permissible, then for state registration of the right it is necessary either to make appropriate changes to the title document (in cases where this can be done within the framework of the law), or to clarify the area of the land plot in court. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 17 Federal Law No. 122, the grounds for state registration of the presence, origin, termination, transfer, restriction (encumbrance) of rights to real estate and transactions with it are acts issued by state authorities or local governments within the framework of their competence and in the manner established by law , in force at the place of publication of such acts at the time of their publication. Thus, amendments to previously issued resolutions (decisions) must also comply with the established norm. For example, in 1994, a citizen was given ownership of a plot of land with an area of 10 acres for personal subsidiary farming in a rural area, with the maximum size of plots provided at that time established in the area being 12 acres. During the current survey, the calculated area of the land plot was 11.5 acres. Since this does not exceed the existing limit, it is possible to make changes to the previously issued resolution in terms of clarifying the area of the land plot. How to remain without land It is much more difficult to clarify the area of a land plot in sales contracts, certificates of inheritance, and other transaction documents. When a notary issues a certificate of the right to inheritance by law or by will, he cannot indicate in it a figure other than the one that indicates the area of the land plot in the testator’s title documents. Although over the decades the fences have been moved many times, and the neighbors don’t seem to mind... There is only one way: clarification of the area, if it exceeds the permissible calculation error, is possible only in court, for example, due to acquisitive prescription (Article 234 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) . Another rather complex legal issue is related to the so-called “additions” to land plots. This is what we are talking about: let’s say that beyond the border of a citizen’s land plot there is free state (or municipal) land, the small area of which does not allow the formation of an independent land plot (for example, only one and a half or two hundred square meters). The citizen himself is not against purchasing an additional piece of land as his property for a fee, but... According to Art. 33 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Land Code of the Russian Federation), the maximum (maximum and minimum) sizes of land plots provided to citizens for ownership from state or municipally owned lands are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation or regulatory legal acts of local government bodies. And these minimum sizes, including land plots for gardening, vegetable gardening, and summer cottage farming, as a rule, exceed six acres! This means that such a transaction would be contrary to the law. The situation is also difficult if the main plot of land was previously provided to a citizen for individual housing construction or for personal subsidiary plots, that is, for purposes related to construction. Then, in order to connect the additionally acquired land plot (“additional plot”) with the main one in the future, these two plots must have the same permitted use, but in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 30 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, the provision of land plots for construction into ownership is possible only through bidding (competitions, auctions)... And who will compete at the bidding for one and a half hundred square meters? As we can see, the problem of clarifying the area of a land plot within limits exceeding the established permissible technical error in calculating areas is currently not regulated by law. It would be possible to use the norm of paragraph 2 of Art. 33 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation that the maximum sizes of land plots provided to citizens for free ownership from lands in municipal ownership are established by regulatory legal acts of local government bodies, and from lands in state ownership - accordingly by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation or federal laws. However, this rule is applicable only after the delimitation of state ownership of land in accordance with the Federal Law “On the delimitation of state ownership of land”, that is, after the compilation and approval of the relevant lists of land plots, the preparation of their cadastral plans, etc. But this Law is practically not applied, because neither the state, nor even the municipalities have the money to carry out this work. There remains hope for the legislative creativity of the new deputy corps of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of Russia... LINKS TO LEGAL ACTS “LAND CODE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION” dated October 25, 2001 N 136-FZ (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on September 28, 2001) FEDERAL LAW dated July 17, 2001 N 101- Federal Law “On the Delimitation of State Ownership of Land” (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on 04.07.2001) FEDERAL LAW of 02.01.2000 N 28-FZ “On the STATE LAND CADASTRE” (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on 24.11.1999) FEDERAL LAW of July 21, 1997 N 122-FZ “ON STATE REGISTRATION OF RIGHTS TO REAL ESTATE PROPERTY AND TRANSACTIONS WITH IT” (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on June 17, 1997) “CIVIL CODE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION (PART ONE)” dated November 30, 1994 N 51-FZ (adopted by the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation F 21.10. 1994) DECREE of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06/07/2002 N 396 “ON APPROVAL OF THE REGULATIONS ON CARRYING OUT TERRITORIAL LAND DEVELOPMENT” “METHODOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CARRYING OUT LAND DEVELOPMENT OBJECTS MOUNTING” (approved by Roszemkadastrom 17.02.2 003) EZh-Lawyer, N 29, 2004
WORKING WITH A CLAIM »
Comments on laws »
Features of calculating the building area
To determine the maximum allowable building percentage, it is recommended to contact a professional. Specialists from relevant organizations will examine the site and calculate the optimal ratio of areas designed for the construction of construction projects and the general territory.
Thanks to ready-made architectural projects with designated parameters of all buildings, as well as the presence of a floor plan, it will not be difficult for experienced specialists to calculate the necessary parameters.
If the project is not ready, you will have to invite a team of topographers to conduct a professional topographic survey. With the help of special programs, they find out the designated area for construction.
What is included in the development area of a land plot?
There is such a thing as “permitted construction area”. This is a regulated value, which is calculated differently for each territory. So, for example, for warehouse areas, the building area is higher than for residential buildings. Therefore, when starting any construction, you must know how to calculate the building area .
Architectural projects indicate all the necessary dimensions, so you can get information for calculations from architectural projects. After all, such projects contain floor plans, which indicate all the necessary dimensions, including the dimensions of external walls.
How to determine the number of storeys of a private house
When determining the number of floors of a house, the number of floors includes all above-ground floors, including the technical floor, attic, and also the basement floor, if the top of its floor is at least 2 m above the average planning level of the ground. Underground for ventilation under buildings on permafrost soils , regardless of its height, is not included in the number of above-ground floors. If the number of floors is different in different parts of the building, as well as when the building is placed on a site with a slope, when the number of floors increases due to the slope, the number of storeys is determined separately for each part of the building. The technical floor located above the upper floor is not taken into account when determining the number of storeys of the building.
(Source SNiP 06/31/2009)
How to calculate the area of premises in a private house. Many people find this difficult to do. I would like to once again draw your attention to the fact that there is no concept of living space in private housing construction. Confusion in terms sometimes leads to unpleasant incidents when designing and registering a house. I hope this article will help you understand what the total area during construction and the total usable area of the house are. In the next article I will talk about the rules and regulations for redevelopment.
I RECOMMEND ALSO READING:
What is included in the development area of a land plot?
2)
The building area
(AZ) is defined as the sum of the areas occupied by buildings and structures of all types, including sheds, open technological, sanitary, energy and other installations, overpasses and galleries, loading areas, underground structures (tanks, cellars, shelters , tunnels over which buildings and structures cannot be placed), as well as open parking lots for cars, machines, machinery and open warehouses for various purposes, provided that the dimensions and equipment of parking lots and warehouses are accepted according to the standards of technological design of enterprises.
Also read: How vacation pay is calculated in 2020 upon dismissal
The construction area does not include areas occupied by blind areas around buildings and structures, sidewalks, roads and railways, railway stations, temporary buildings and structures, open sports grounds, areas for workers' recreation, green spaces (trees, shrubs, flowers and grasses) , open parking lots of vehicles owned by citizens, open drainage and other ditches, retaining walls, underground buildings and structures or parts of them, above which other buildings and structures may be located.
What is included in the development area of a land plot?
The construction area does not include areas occupied by blind areas around buildings and structures, sidewalks, roads and railways, railway stations, temporary buildings and structures, open sports grounds for workers' recreation, green spaces (of trees, shrubs, flowers and grasses), open parking lots of vehicles owned by private individuals, open drainage and retaining walls, underground buildings and structures or parts thereof, above which other buildings and structures can be located, as well as excess parking areas and warehouses in excess of the allotment standards.
The subject of development is an object completed by construction and ready for delivery, i.e. finished commercial construction products of a construction and installation or other organization. A free plot of land is allocated for development, the part of which occupied by buildings is called the building area of the building or facility. The rest of the allocated land plot remains temporarily unused and reserve.
Summarize
As you can understand from the article, there are different types of area. All of them are equally important and are required in certain cases. To carry out calculations correctly, you need to know the current legislation. It spells out all the rules and regulations that must be followed. The building area itself is an integral part of every house project. It must meet standards in order for the project to be approved and then implemented.
If there is a ready-made architectural project, then it will not be difficult to find out the question of interest. Everything is spelled out in this document, and a person will be able to read what is necessary in it. But, if there is no such document, then you will have to get the answer to the question yourself. And for this, the information from the article will be useful.