Recently, an updated procedure has been established for how the composition and properties of wastewater are monitored. The main document that lists the updates is Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 728 dated May 22, 2020. In addition, this Decree introduced some changes to certain regulations. Without a doubt, this is a fairly significant change in environmental legislation; there are many questions.
The question remains relevant of how the control of wastewater sent to the centralized wastewater system (CSS) will now be carried out, because the previous Rules have lost force. We have studied the innovations and in this material we will try to pay attention to the main aspects of this issue.
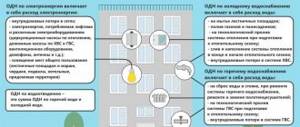
- Who controls the composition and properties of wastewater?
- What has changed in drainage in 2020?
- What does monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater include in 2020?
- Frequency of water disposal control
- Fines for water users
Calculation of drainage according to the standard
‘);} //—>
');} //—> Water disposal according to the standard is the amount of wastewater discharged by the consumer into the sewerage network without installing water meters in a house or apartment. The formula for calculating water disposal according to the standard: P = n * N * T * k, where P is the price of water disposal in rubles; n is the number of people living in the house or apartment; N - standard water disposal per person; T—water disposal tariff in rubles per m3; k—increasing factor (if available). See also - balance of water consumption and wastewater disposal. You can quickly perform this economic (accounting) calculation using our online program. To do this, enter the initial value in the appropriate field and click the button.
This page presents the simplest online calculator for calculating sewerage according to the standard, depending on the number of residents, the standard, the tariff and the increasing factor. To calculate the cost of sewerage according to the standard, you need to know the tariff, standard, number of residents and the need to apply an increasing factor.
The housing and communal services receipt, among other things, includes an item on payment for water drainage. It includes not only the sewage system, but also the water that flows into the drain holes of the bathtub and sink. Water disposal is calculated using special formulas. The calculation method depends on whether you have water meters.
What is the standard for water disposal?
Water consumption and water disposal for the population are interconnected concepts that cannot coexist without each other. But if water consumption standards are more or less clear, then what are water disposal standards? This is the average daily amount of wastewater per resident of an apartment building. And when we are talking about an enterprise, the unit in question is calculated according to the number of products produced.
Sewage, in essence, is the discharge of water, with the help of which all waste is removed outside the populated area where the house is located. Depending on what kind of waste we are talking about, it can be sent for treatment to specialized places. There are several degrees of water pollution:
- Conditionally clean, that is, it meets the standards;
- Requiring cleaning.
To determine the standard of water disposal, it is necessary to review the indicators every five years. Technologies in this industry are developing quite quickly, which is associated with an increased standard for those people who do not install meters. As for the average standards, the following values can be distinguished:
- from 25 liters per day to 45 liters of daily allowance per resident, if the house is not connected to water and sewerage;
- from 125 l to 160 l per person, if the house is connected to sewerage and water supply, but bath costs are not taken into account;
- from 160 l to 230 l per person, if the house has a bathtub and is connected to water supply and sewerage;
- from 230 l to 350 l per person, if a centralized hot water supply is also connected to the house.
But these are very conditional indicators, which, as already mentioned, are recalculated every five-year period.
What is drainage
There is a clear formulation of this service. It is enshrined in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 354 of 05/06/2011. This is a set of procedures that is needed to remove household wastewater from apartments through the connection network. The process of removing and filtering water has several stages. When a meter is installed, the indicator is calculated based on the water used and the regional tariff. Every citizen-consumer must pay for sewerage.
In other words, water disposal is the purification of water and disposal by discharge into the sewer. Draining water when washing your face, after a shower, or from the dishwasher is all water drainage.
Water disposal is regulated on the basis of the following documents:
- Law on water supply and sanitation (dated 07.12.2011 N 416-FZ)
- Official regulations and orders at the local and regional level;
- Internal provisions of city water utilities.
Changes in legislation on water supply and sanitation
In the article we will look at what has changed in Federal Law No. 225-FZ of July 29, 2017 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Water Supply and Sanitation” and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” (will come into force on January 1, 2019; hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 225 -FZ) in the legislation on water supply and sanitation.
Federal Law No. 225-FZ introduced amendments to the following regulatory legal acts:
• Federal Law No. 416-FZ of December 7, 2011 “On Water Supply and Sanitation” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 416-FZ);
• Federal Law No. 7-FZ of July 10, 2002 “On Environmental Protection” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 7-FZ;
• Federal Law No. 166-FZ of December 20, 2004 “On Fisheries and Conservation of Aquatic Biological Resources” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 166-FZ);
• Water Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Water Code of the Russian Federation).
New concepts
Federal Law No. 225-FZ introduced the following concepts:
• local treatment plant - a structure or device that provides treatment of the subscriber's wastewater before it is discharged (discharged) into the centralized water disposal (sewage) system;
• standards for the composition of wastewater - indicators of the concentration of pollutants in the subscriber's wastewater discharged into the centralized drainage (sewage) system established for the purpose of protecting water bodies from pollution;
• centralized water drainage system of a settlement or urban district - a complex of technologically interconnected engineering structures designed for drainage from the territory of a settlement or urban district.
It also follows from the text of Federal Law No. 225-FZ that technologically regulated substances mean substances for which technological indicators of the best available technologies (hereinafter referred to as BAT) are established.
Changes to Federal Law No. 416-FZ
Numerous changes to Federal Law No. 416-FZ are mainly related to the translation of permissible discharge standards (hereinafter - VAT) for subscribers of centralized wastewater systems (hereinafter - CSV) into standards for the composition of wastewater.
At the same time, standards for the composition of wastewater are established for subscribers of organizations engaged in wastewater disposal. Requirements for the composition and properties of wastewater discharged into water bodies by organizations engaged in wastewater disposal are established in accordance with water legislation, legislation in the field of environmental protection and legislation in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population.
Wastewater composition standards
To replace the environmental ch. 5 of Federal Law No. 416-FZ introduces a new chapter. 5.1 “Regulation of wastewater discharge into centralized water disposal (sewage) systems” .
Thus, in order to protect water bodies from pollution, standards for the composition of wastewater are established for the facilities of subscribers of organizations engaged in wastewater disposal. The specified standards are established for any subscriber facilities, with the exception of:
• residential buildings;
• apartment buildings (except for non-residential premises in apartment buildings that have separate sewer outlets in the central sewer system);
• other facilities defined by the rules of cold water supply and sanitation approved by the Government of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Rules).
BY THE WAY
At the moment, the Rules for Cold Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 2013 No. 644, do not differentiate between subscribers on the need to establish VAT depending on the volume of wastewater discharged; The categories of such subscribers are introduced by Ch. 5 of Federal Law 416-FZ, which will become invalid as of 01/01/2019. Perhaps, in the same vein, a category of subscriber facilities will be defined that fall under the wording “other facilities”, which will not be affected by the establishment of standards for the composition of wastewater.
Standards for the composition of wastewater are established by local governments of urban settlements and urban districts for the organization of water supply and sanitation.
In this regard, the Government of the Russian Federation will have to adjust the Rules, which from 01/01/2019 will have to determine, among other things:
• the procedure for establishing standards for the composition of wastewater by local governments;
• features of establishing standards for the composition of wastewater in relation to technologically regulated substances;
• the procedure for calculating fees for the discharge of pollutants in wastewater in excess of the established standards for the composition of wastewater and collecting the specified fee from subscribers, the procedure for reducing the fee for subscribers for the discharge of pollutants in wastewater in excess of the established standards for the composition of wastewater in the event that subscribers implement reduction plans discharges.
Discharge Reduction Plan
The discharge reduction plan is not new, but it will no longer apply to subscribers subject to discharge limits.
Subscribers who exceeded the standards for the composition of wastewater 2 or more times within 12 months from the date of the first excess, and subscribers who allowed a single excess of the standards for the composition of wastewater 3 or more times, are obliged to within 90 calendar days from the date of notification of the subscriber by the organization carrying out water disposal, about such a violation, develop a plan for reducing discharges and approve it after agreement with the territorial body of the federal executive body exercising state environmental supervision (if the subscriber’s facility meets the criteria for determining objects subject to federal state environmental supervision), or with the authorized executive body authorities of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation (in other cases), as well as with the organization carrying out wastewater disposal, and implement a plan for reducing discharges within the time frame provided for by this plan.
Other subscribers have the right to develop and approve a discharge reduction plan.
Requirements for the content of the discharge reduction plan, the procedure and timing for its approval will be established by the Government of the Russian Federation. So far, the activities included in the plan have only been outlined.
If the subscriber does not have a discharge reduction plan developed and agreed upon within the period specified above, or if it is not implemented, as well as in the case of repeated (2 times during the year) the subscriber does not allow representatives of the organization carrying out wastewater disposal to the place of wastewater sampling for carrying out in the established manner in order to control their composition and properties, the organization carrying out wastewater disposal, within 15 calendar days after the expiration of the specified periods or from the date of the second non-admission, informs the relevant state environmental supervision body about this. And this is the basis for checking the subscriber and bringing him to justice.
Let's hope that the accepted deadlines for approval by Rosprirodnadzor will not affect plans to reduce discharges and will not affect the subscriber's ability to fulfill the will of the legislator.
NOTE
Federal Law No. 225-FZ burdens subscribers with the responsibilities of developing, approving and implementing two plans at once - a plan for reducing discharges and a plan for ensuring compliance with the requirements for the composition and properties of wastewater (in cases established by the Rules).
Payment for excess discharges
The procedure for calculating fees for excess discharges remains unchanged for now (but changes to the existing procedure may be made by the Rules). At the same time, the wording regarding the payment by subscribers of a fee for negative impact on the environment (hereinafter referred to as NVOS) has traditionally changed. Thus, in relation to pollutants discharged into the wastewater treatment plant, subscribers do not pay for the NWTP when discharging pollutants as part of wastewater into water bodies.
Payments for excess discharges are made by subscribers of the wastewater disposal organization in the manner prescribed by the Rules.
The rules will set out other aspects of charging.
Changes to Federal Law No. 7-FZ
Standardization of discharges from central waste water facilities of settlements or urban districts
Federal Law No. 225-FZ gives a new version of clause 5 of Art. which has not yet entered into force. 23 of Federal Law No. 7-FZ (in a more specific, rather than referential version).
Thus, for wastewater treatment facilities in settlements or urban districts classified as Category I facilities, a comprehensive environmental permit (hereinafter referred to as IEP) establishes technological standards based on technological indicators of best practices in the field of wastewater treatment using wastewater treatment facilities in settlements or urban districts, established by the Government of the Russian Federation on based on the information and technical reference book on BAT in the field of wastewater treatment using wastewater treatment plants of settlements or urban districts, taking into account the capacity of treatment facilities of wastewater treatment facilities of settlements or urban districts, as well as the categories of water bodies or parts thereof into which wastewater is discharged.
The rules for classifying water bodies as water bodies for the purpose of establishing technological indicators of BAT in the field of wastewater treatment using wastewater treatment plants of settlements or urban districts are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
In addition, Art. 23 of Federal Law No. 7-FZ will be supplemented with clause 5.1, according to which for objects of central water supply in settlements or urban districts classified as objects of category II, in the event of the issuance of an IEC for them in relation to technologically regulated substances, technological standards are established in the manner prescribed for objects of I categories.
Clause 7 of Art. 23.1 of Federal Law No. 7-FZ has also changed from reference to become specific: if it is impossible to comply with technological standards (VAT of technologically regulated substances), temporarily permitted discharges are established for the objects of wastewater treatment plants in settlements or urban districts based on the actual mass indicators of pollutant discharges at the level of maximum concentration values for the last calendar year of operation of central water supply facilities in settlements or urban districts (excluding emergency discharges).
As a result of the addition of clause 2 of Art. 44 of Federal Law No. 7-FZ, when planning and developing urban and rural settlements, measures must also be taken to ensure, incl. using central water treatment systems, collection and purification of rain, melt, infiltration, irrigation, and drainage waters, the drainage of which is carried out from the territories of settlements.
Environmental efficiency improvement program, environmental protection action plan for central heating facilities in settlements or urban districts
Let us recall that the Federal Law of July 21, 2014 No. 219-FZ “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Environmental Protection” and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” introduced a requirement for the need to develop programs to improve environmental efficiency (for Category I facilities) and plans environmental protection measures (for objects of categories II and III).
Federal Law No. 225-FZ specifies the norms of innovations that have not yet entered into force. A separate range of changes to Federal Law No. 7-FZ is associated with the need to take into account new forms for CSV objects of settlements or urban districts in the current legislation. The relevant standards have added the need to take into account or include in the package of documents required for the period of gradual achievement of standards, a program to improve environmental efficiency or an environmental action plan.
Article 67.1 (will come into force on 01/01/2019) of Federal Law No. 7-FZ is supplemented by clause 13: programs for increasing environmental efficiency, plans of measures for environmental protection of organizations operating central heating systems of settlements or urban districts are developed and approved for the period of gradual achievement of the corresponding technological standards and VAT of technologically regulated substances.
Information on wastewater treatment using waste water treatment systems in settlements or urban districts, information on programs to improve environmental efficiency, plans for environmental protection, and the results of the implementation of these programs and plans at least once a year are published by the local government body in the media and posted on the official website. website of the municipality (if such a website does not exist, on the website of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation).
Payment for environmental pollution for discharges of pollutants by organizations operating wastewater treatment plants in settlements or urban districts. Compensation for environmental damage
Article 16.3 of Federal Law No. 7-FZ is supplemented by clause 6.1, which introduces additional coefficients when calculating fees for discharges of pollutants by organizations operating wastewater treatment plants of settlements or urban districts when discharging pollutants that are not related to substances for which BAT technological indicators are established in the field wastewater treatment using wastewater treatment plants for settlements or urban districts.
It has also been determined that the following will be deducted from the amount of payment for environmental waste when discharging pollutants from organizations operating wastewater treatment plants in settlements or urban districts:
• costs for the implementation of measures to reduce environmental pollution included in the environmental efficiency improvement program or environmental protection action plan, actually carried out by the specified organizations, within the calculated payment for environmental pollution in relation to all pollutants, when discharged by the specified organizations, payment for environmental pollution is paid;
• the amount by which the payment of subscribers of these organizations for the discharge of pollutants in wastewater in excess of the established standards for the composition of wastewater was reduced.
The specified costs of organizations operating central heating systems in settlements or urban districts, and the amount not taken into account when calculating the fee for NVOS in the reporting period, are taken into account in subsequent reporting periods, incl. outside the deadlines for implementing an environmental efficiency improvement program or environmental action plan.
Also, Federal Law No. 7-FZ is supplemented by Art. 78.1 “Features of compensation for damage to the environment when discharging pollutants through centralized sewerage systems of settlements or urban districts” , according to which the damage is compensated in full by subscribers of the centralized water supply system, and if the cause of harm (subscriber) is unknown - by organizations operating the centralized water disposal systems of settlements or urban districts districts.
A reference to the procedure for compensation for damage established by the Government of the Russian Federation allows us to assume that damage will be compensated by organizations operating water treatment plants in a special order, and not as now - according to the Methodology for calculating the amount of damage caused to water bodies due to violation of water legislation, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia dated April 13, 2009 No. 87 (hereinafter referred to as the Methodology), according to which hundreds of millions of rubles are billed. This thesis is confirmed by the changes made to the RF CC.
Changes to the Water Code
The RF Water Code includes a requirement to comply with technological standards.
It is also noted that the Methodology should take into account the specifics of compensation for damage caused to the environment when pollutants are discharged into water bodies through the water supply centers of settlements or urban districts, established by the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of water supply and sanitation.
At the same time, the ban on the discharge of wastewater within the boundaries of fishery protection zones is excluded.
Changes to Federal Law No. 166-FZ
Federal Law No. 225-FZ introduced a change that is not related to the general topic of changes, but is very important in its essence.
Thus, the changes made to Federal Law No. 166-FZ are aimed at correcting the current situation, when any drainage ditch in an industrial zone can be recognized as an object of fishery importance:
| Federal Law No. 166-FZ (in this edition) | Federal Law No. 166-FZ (as amended by Federal Law No. 225-FZ) |
| Article 17. Fishery basins and water bodies of fishery importance […] 3. Water bodies of fishery significance include water bodies that are used or can be used [1] for the extraction (catch) of aquatic biological resources. […] | Article 17. Fishery basins and water bodies of fishery importance […] 3. The criteria and procedure for classifying a water body or part of it as a water body of fishery importance, the procedure for determining the categories of water bodies of fishery importance are established by the Government of the Russian Federation. […] |
In this case, on 01/01/2019, clause 4 p. 17 of Federal Law No. 166-FZ, according to which the categories of water bodies of fishery importance and the characteristics of the extraction (catch) of aquatic biological resources living in them are established by the federal executive body in the field of fisheries.
Let's hope that the normative act establishing the criteria for classifying a water body or part of it as a water body of fishery importance will adequately distribute water bodies into fish and non-fish categories, without leading to absurd situations when an enterprise uses non-fish objects or even is located in the area where they are located.
Conclusion
Since the stated effective date of the changes is 01/01/2019, the new rules do not have any legal consequences yet. It is worth keeping in mind that significant changes may arise when the Rules are brought into compliance with Federal Law No. 225-FZ. However, given that the effective date of previous changes was moved several times but never arrived, there is no need to rush into thinking about how to comply with the new rules. They may also be changed.
[1] Emphasis added.
How is this item shown on receipts?
Many people believe that the drainage of water resources includes only discharge into the sewerage system. In reality, the service includes the removal of a water resource after use and delivery to treatment facilities, its filtration, and so on.
If we talk about the monthly display of consumption, then if IPU is installed, the item is called - cold water supply (cold water supply) and hot water supply (hot water supply). If there is no IPU in the apartment, then the calculation is carried out based on the standards at the local level. This will appear on the receipt as follows:
- Cold water supply at OI MKD - consumption of cold water in the house;
- DHW t/n at OI MKD – hot water (volume);
- DHW heating at OI MKD - hot water (heat).
The procedure for calculating charges without a counter
If there is no meter in the apartment, all expenses are charged at the average rate. The tariff is based on average consumption standards, which are always higher than real ones. Average tariffs are also set by local governments.
The calculation takes into account the square footage of the room, the presence of a bath, shower, etc. Then the rate per person is multiplied by the number of registered citizens, and this amount is indicated in the payment receipt.
You can find out the tariffs on the website of the management company or local authorities.
How to calculate water drainage using a meter: formula and example
To calculate water drainage from a meter, you need to use a special formula:
SV = (DHW + cold water) x TV, where
SV – total amount to be paid; DHW – monthly hot water consumption, based on the IPU reading, m3; Cold water consumption - monthly consumption of cold water according to the meter, m3; TV – regional tariff.
This calculation is regulated by the Government Decree “On the procedure and conditions for citizens to pay for housing and utilities.” The regional tariff for each subject of the Russian Federation is individual.
For example, let’s calculate the cost of the service in Moscow. The local regional tariff (TV) is 21.90 rubles/m3. The monthly consumption indicator according to the meter is 10 cubic meters of cold water and 5 cubic meters of hot water. The total consumption of hot and cold water supply is 15 m3.
Substituting known values into the formula, we get:
(5 + 10) x 21.90 = 328.5 rubles.
The owner must repay such an account by the 20th of the next month.
If your sewer payment is late, the city water utility will issue a fine. If repayment of the debt is delayed, the organization will consider that its rights have been violated. Penalties will be accrued daily.
For those who do not want to calculate water drainage by meters themselves, there are specialized portals where you only need to enter the readings. Next, the system will display the amount to be paid.
In case of any controversial situations, you must immediately contact the Management Company for clarification. For example, if after an independent calculation it turns out that the resulting amount is less than that calculated by the city water utility. There have often been cases when employees of the Criminal Code took advantage of the inattention of conscientious citizens and entered increased testimony.
How is the fee calculated if there is no meter: example
When there is no meter, the amount on the receipt increases. Thus, monthly consumption will be calculated based on regional standards. There is no need to explain that government standards significantly exceed actual water consumption.
The calculation is made using the formula:
Regional standard * number of registered people in residential premises * tariff.
For example, in Moscow the regional standard is 11.68 m3 per person per month. It is calculated based on the standard for hot water - 4.745 m3 and cold - 6.935 m3.
Registered citizens – 2.
The regional wastewater tariff in Moscow is 21.90 rubles/m3.
Fee calculation: 11.68 * 2 * 21.90 = 511,584 rubles.
The owner will have to pay this amount if he does not have an IPU installed. After submitting the data, the payment center checks the correctness of the calculated indicator and issues a payment order. A payment slip with the estimated amount will arrive in the new month.
Nuances
It must be remembered that owners of residential real estate in apartment buildings pay not only for their own consumption, but also for common household consumption. This is the case if the house has a collective metering device (KPU). Then the payment will be calculated based on the overall indicator of each apartment. If the total readings are less than the consumption readings of the entire house, the difference is distributed among all residents of the house.
If a high-rise building does not have communal meters, residents do not have to pay the difference. This is reflected in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 334 of April 16, 2013. We should expect a review of this order, because this decision has been submitted for consideration.
The full text of the Resolution can be downloaded here.
By the same decree, the Government of the Russian Federation abolishes the fixed indicator of the general needs of a home. Therefore, it should not be reflected in the payment. If this happens, then the owner has every right to file a complaint against the management company and demand a recalculation. In this case, the readings from the IPU should be taken as a basis. However, this is only if this clause is not specified in the service agreement. Therefore, you must first study the concluded document.
When paying for housing and communal services, owners are charged a commission of 2-3%. The Government issued such a resolution in 2009.
Every decent owner pays utility bills monthly and has the right to count on quality services. If, in his opinion, water drainage services are performed poorly or do not suit the tenant, he has the right to demand a recalculation.
To do this, it is necessary to collect supporting documents that prove the fact of poor quality services. All facts of this kind must be recorded. If this is not done, it will be difficult to prove anything.
If a water leak occurs, the owner is responsible. According to the law, it is he who is responsible for the serviceability of his property. However, when the leak occurred due to the fault of the utility companies, the water bill will be paid by the housing and communal services. Especially when the system is working properly or the housing is new. If the payment arrived without taking this fact into account, there is every reason to write a complaint to the housing and communal services and demand a recalculation.
Useful article? Rate and share with friends!
Frequency of water disposal control
Control can be planned or unscheduled. Let's look at its differences.
Scheduled control is carried out no more than once per calendar month and less than once per calendar year. An exception is for subscribers whose facilities discharge a volume of less than 30 cubic meters per day in general (if wastewater is discharged into the sewer system). The frequency of planned control in this case cannot be more than once a calendar month.
As for unscheduled control, it is mandatory if:
- An accident has occurred, or the central heating system or its elements have failed;
- During state environmental supervision, violations were identified and orders were received to eliminate them;
- The water body was contaminated by the water supply system at the point where wastewater was discharged into it.
How to calculate water disposal by meter and according to sewerage standards per person
Water disposal is included in the receipt for housing and communal services without fail, which means that all consumers must pay for this service in the same way as for other resources. At its core, this service consists of removing used water from premises, purifying it and further recycling it.
Owners of not only apartments, but also some owners of private houses are required to pay for sewerage. It is important to understand that drainage does not only mean the sewer system. The service includes draining the used resource, diverting it from housing, transportation, direct disposal and cleaning for reuse.
The water supply and sanitation system is currently regulated by the relevant law, adopted on December 7, 2011. It also reflects the requirements for the service provided and the rules for quality control thereof. In addition to this law, in this matter one should also refer to the regulations that regulated it previously, namely government regulations, regional acts, regulations of territorial organizations of suppliers.
Since we are talking about a separate category of utility services, consumers need to know how sewerage is calculated and what the differences are between calculations with and without metering devices.
Dear readers!
Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right →
It's fast and free! Or call us by phone (24/7):
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call us by phone. It's fast and free!
+7 Moscow, Moscow region St. Petersburg, Leningrad region Regions (free call for all regions of Russia)
Algorithm of actions for individuals and legal entities
For an individual:
- Installation of a metering device followed by commissioning.
- Submitting an application with a set of documents (copy of passport, certificate of ownership).
- Signing of both copies of the agreement within a certain period.
For a legal entity:
Installation of a water meter, putting it into operation.- Submitting an application, accompanied by a set of documents (the list of documents required to be submitted to the organization can be found on the official website or by calling the supplier).
- Receiving two copies of a standard contract for consideration.
- Drawing up a protocol of disagreements (if necessary).
- Signing and handing over one copy to the supplier.
Rules for calculating consumed resources
If you are interested in the question of how to calculate drainage, you must be guided by the following rules:
- In accordance with the thirteenth paragraph of Government Decree of the Russian Federation No. 392 of July 30, 2004, to determine the amount of payment, an established formula is used, where the tariff for sewerage adopted in the region is multiplied by the size of the resource consumed;
If there are installed individual meters for hot and cold water in the apartment, their indicators are used in the formula; when calculating per person without a meter, the average indicators adopted by local governments are used;- If sewerage meters are available, the number of cubic meters of hot water is multiplied by the regional tariff, taking into account VAT, after which the number of cubic meters of cold water is multiplied by the same tariff and these two results are summed up, which is the amount payable;
- In the absence of meters for metering resource consumption, standard standards for the locality are applied, regardless of how much the consumer actually uses and whether he uses it at all;
- Current standards are reviewed annually and published on the official websites of local administrations, as well as in local media;
- When it comes to an apartment building, common house meters are taken into account, if any.
Fines for water users
View fines for water users
The size of fines for water users depends on the nature of the violation. Water pollution can even threaten the water user with criminal liability. Fines will not affect you only if you comply with environmental legislation and have all the permits required by the enterprise. EcoPromCenter specialists will help you with any issue of water use!
At the time of writing, changes are still being made. For subscribers with wastewater disposal of less than 30 cubic meters per day, the fee is 20,000 rubles/month. In addition, it is planned to introduce a new service regarding payment for environmental damage to wastewater networks. It should be taken into account that it is necessary to wait for the final results of the changes to fully understand how water users will have to report.
Tariff formulas
To summarize the above, the formula by which the amount payable for sewerage is calculated is as follows:
(cold water supply + hot water supply) *territorial tariff.
So, when the total cost of hot and cold water supply for the past month is thirty cubic meters at a tariff of eighteen rubles - 30 * 18 = 540 - this is exactly how much you will have to pay.
It is in the interests of each consumer to independently control the standards of consumed resources and the required payment amounts. Management companies sometimes take advantage of the inattention of the population and their low legal awareness, so before making a payment it would be a good idea to check the figures on the receipt with the real numbers. So, for example, if the receipt states that eight cubic meters of cold water were consumed per month, and nine cubic meters of hot water, which is equal to twenty in total (although it should be seventeen), the consumer has the legal right to complain to the management company in court.
In reality, paying by meter installed for the entire house is not such a common occurrence today. However, all residents of an apartment building where such a metering device is available have the right of access to its readings. Although, on the other hand, it is impossible to calculate from it exactly who used it and how much; this requires only individual counters.
Orientation by receipts
If common house meters or individual metering devices are installed in the apartment, there is no problem in calculating the amount to be paid, knowing a simple formula and using the example calculations given above. In the absence of meters, as mentioned above, regional standards apply. In this case, you don’t need to count anything at all; all the information will be displayed on the receipt.
By studying the information presented in the receipt, which is sent to all consumers every month, you can find out whether the apartment building has common meters. So, if these are installed for hot and cold water, the receipt will contain such designations as GV DPU and HVS DPU. In this case, you will have to multiply the regional sewerage tariff not by the indicators of your personal meters in the apartment, but by the indicators of the common household one.
General household needs, such as cleaning the territory and entrances, are also deducted from the readings of joint metering devices. If there are no such devices, but there are individual meters in the apartment, this will be reflected in the receipt with the marks GV IPU and HVS IPU.
For all controversial and other issues that arise upon receipt of a receipt for payment, regardless of the presence of a meter, you must contact the management company directly.
Procedure for payment for sewerage and standards with estimated tariffs
In apartment buildings, the management company receives payment for services. Charges are monthly, the general rules are as follows: the amount of water consumed is equal to the amount of discharge into the sewer.
New procedure for calculating garbage fees for residents of apartment buildings
The tariff is set by the regional authorities, the value directly depends on the degree of deterioration of the system, treatment facilities and other equipment necessary for wastewater disposal and disposal. The fee also includes the cost of wages for emergency crews and maintenance personnel.
Consumer rights
When navigating how to calculate water drainage using a meter, it is important to know that in addition to the obligation to timely and fully pay for utilities, which includes sewerage, every consumer has the right to receive quality services. If they are not provided or do not meet the requirements established by Russian legislation, every citizen has the right to demand a recalculation.
Preparation of documents for filing a complaint:
- Independent written calculations of the required fees in accordance with the attached receipts;
- Official report of the management company for the current year;
- Planned expenses of the management organization for the next year (estimates, copies of related documentation);
- Information about the income and expenses of the management company.
In order for recalculation for low-quality services to actually be made, it is necessary to provide recorded evidence that they were actually provided of low quality, which violates legal norms, and from what period. All provided utilities are calculated for a certain time period, so if it is not recorded, it will not be so easy to prove anything.
What does monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater include in 2020?
After Regulation No. 728 came into force, wastewater control includes the following steps:
- Conducting wastewater sampling;
- Further analysis of collected wastewater samples;
- Visual control (more precisely, this means checking objects for compliance with the requirement to prohibit discharge into a centralized drainage system).
Please note that visual control is a new stage. It is carried out in accordance with Rules No. 644 and Rules No. 728 on substances, waste, wastewater, for which verification of compliance with the requirements for banning said discharge is possible without sampling wastewater and further analyzing it. This procedure is carried out if prohibited discharges into the central heating system can be visually detected. These substances are in the list of Appendix No. 4 to Rules No. 644.
The actual indicators of wastewater are determined using special sampling equipment, which is installed by the organization carrying out wastewater disposal.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with what the wastewater sampling report form is.
Visual inspection, wastewater sampling and analysis of collected wastewater samples
We propose to dwell in a little more detail on what visual control is, as well as such control stages as wastewater sampling and analysis of already collected samples.
Who is responsible for each stage of wastewater control?
- Visual control is carried out by the wastewater disposal organization;
- According to special requirements, wastewater sampling is carried out by an accredited laboratory or wastewater disposal organization;
- Also, an accredited laboratory analyzes already collected samples.
Requirements for subscribers:
- Provide the opportunity to conduct visual inspection and sampling of wastewater;
- Provide free access to water for monitoring;
- Give the wastewater organization free access to the sewerage system;
- Provide places for sampling wastewater and install special signs that will identify control sewer wells (they should not interfere with the installation of equipment);
- The subscriber or his representative must be present during visual inspection.
The form of the act of detecting the fact of discharge of substances that are prohibited for discharge into the water supply center.