What merges
All wastewater collected by the drainage system in populated areas differs in the type of pollution and origin. There are drains:
- household (household or fecal);
- production (technical);
- atmospheric (after melting snow, rain).
The first type of wastewater is water from sinks and washbasins, from taps and toilets, from showers, baths and laundries. This stream mixes both relatively clean liquid and water contaminated with physiological products of human activity (feces). Such wastewater contains organic (plant and animal origin) and mineral impurities:
- biologically significant elements (nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, carbon);
- pathogenic biological agents (microbes, bacteria);
- inert substances (particles of soil, sand, clay, acid, salt and alkali).
Because of this composition, domestic wastewater is considered the most polluted.
Industrial wastewater is varied in composition and impurity content; it contains production losses and waste, remnants of raw materials and reagents. Polluted industrial waters are:
- inert;
- unstable;
- toxic.
The wastewater transported by the industrial wastewater system contains the following contaminants:
- mineral (they most often comply with the standards for release into the reservoir, so they do not undergo additional processing);
- organic (they are processed in treatment facilities);
- mixed.
Mixed industrial wastewater is discharged into the system on a general basis, if it does not contain:
- impurities that can clog pipes or form deposits on their walls (cotton wool, gypsum, scale, fibers);
- substances that have a destructive effect on the material of pipelines and sewerage structures;
- flammable and gaseous additives, which can cause an explosion in drainage networks.
An important requirement for industrial wastewater discharged into the city treatment system: its temperature should not exceed 40C.
Water enters the drainage complex after rain falls, snow melts, and street watering occurs. Such streams are often contaminated with impurities from industrial enterprises, therefore, from certain areas, atmospheric wastewater is treated in the same way as industrial wastewater. Relatively clean wastewater is removed from the streets through special drainage networks.
How to calculate water drainage using a meter
The calculation of fees for wastewater disposal includes several important indicators and is determined taking into account the specifics of the region. The amount payable is calculated in the following ways:
- based on the readings of an individual water meter, which determines the volume of its supply, and installed in a separate apartment;
- according to data from common house metering devices;
- according to established standards.
Of these three methods, the most beneficial option for the user is with a personal water meter in the apartment.
Tariff for payment for sewerage in an apartment building
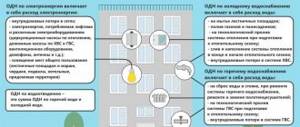
In the Russian Federation there is no uniform tariff for wastewater disposal in apartment buildings, since the price depends on several characteristics:
- climate of the region - the level of payment increases for cold regions, since it requires utility structures to increase the cost of maintaining communications;
- degree of deterioration of the sewer system;
- condition of water supply networks;
- remoteness of farm facilities;
- location of pumping units;
- number of connected consumers;
- the volume of costs for the work of emergency workers and utility workers.
Taking into account the combination of these factors, the tariff for wastewater is set by decree of regional authorities.
Water metering devices
In addition to calculation using the formula, specialized accounting devices are used to determine the volume of wastewater.
But with the introduction of such equipment, difficulties arise due to the need to allocate additional funding for the purchase and installation of meters.
Equipment that takes into account the volume of wastewater is divided into the following categories according to its operating principle:
- ultrasonic;
- electromagnetic;
- mechanical (lever or pendulum).
Ultrasonic devices are the most economical to account for, but are expensive to purchase, which explains their low popularity. The best option is an electromagnetic meter, with acceptable measurement results at a reasonable price.
The most popular devices are mechanical, due to their low cost. Their disadvantage is the low accuracy of wastewater flow measurement.
Calculation of the cost of wastewater disposal
The calculation is performed using the formula:
OS = (PHV + PGV) x T, where
- OS – amount of payment for wastewater;
- PCV and PGW - monthly payments, respectively, for cold and hot water supply;
- T – tariff assigned for wastewater disposal.
The payment is calculated monthly and entered into the receipt as a separate expense item.
What types of systems are there?
Drainage systems differ in their operating principles. Stand out:
- All-alloy.
- Completely separate.
- Incomplete separate.
- Semi-separated.
- Combined.
All water - domestic, industrial, atmospheric - is discharged through the general alloy network. The wastewater is sent through the pipeline to treatment facilities, but in case of heavy rainfall from the main collector, part of it (a mixture of atmospheric and sewage) is discharged into reservoirs without treatment through special storm drains. This system has one significant advantage: it is a short-length pipeline, its installation and maintenance require minimal costs, and the operating requirements are simple.
Also, the all-alloy system is equipped with large-diameter pipes with a reserve volume to allow a significant volume of water to pass through. Disadvantage: frequent clogging of pipes in dry months, pollution of water bodies due to the release of mixed rain, domestic and industrial water into them, danger of flooding with sewage in the lower levels of buildings during periods of heavy rainfall.
In a complete separate system, water flows are usually transported through two networks: separately - domestic and industrial, separately - rain. In cases where industrial wastewater requires several treatment methods, which makes it impossible to connect it with fecal wastewater, the system includes a larger number of networks.
With separate disposal, atmospheric water is most often discharged into reservoirs without treatment. Disadvantage: considerable length with the need to use a large number of pipes, as well as the complexity of their operation.
In an incomplete separate configuration, there is only one network for transporting wastewater and wastewater to wastewater treatment plants. Transportation of wastewater after precipitation directly into the reservoir is carried out through ditches, open trays and ditches.
For a semi-separate drainage system, two networks are provided: one for domestic (domestic-fecal) and industrial wastewater, and one for rainwater (atmospheric). In areas where these networks intersect, separation chambers are located.
If there are few rain streams, they are mixed with household waste and sent to treatment plants. Abundant atmospheric water is mostly transported directly to reservoirs, although a certain percentage (liquids concentrated at the bottom of pipelines) also flows into sewers for treatment.
In the semi-separate complex, economic and domestic wastewater, as well as the most polluted rainwater from the bottom stream, are treated. This configuration copes well with protecting reservoirs from pollution. The disadvantage is the high cost of treatment facilities and significant operating costs.
The presence of a combined complex is justified in large populated areas, where some areas may have a general rafting network, others - an incomplete one, and still others - a completely separate one. In such cases, part of the drainage works with common wastewater, and part with separate networks.
Tariffs for sewerage
Now let's think about what and how much we pay for.
Let's return to the water that enters our apartments and houses. You've probably heard that water is chlorinated somewhere. This is at a minimum and it is a well-known truth. However, the whole process, which is called water treatment, is actually complex and consists of multi-level filtration, disinfection (not only with chlorine) and supply to consumers.
And all these stages require payment - electricity for operating pumps, consumables (filtering and disinfecting), payment for the work of specialists.
If we consider hot water supply, then there is a heating process, which is expensive. Moreover, the heating is constant, because it is unknown when the consumer will want to wash his hands with hot water. And we need to pay for all this.
And here is the drainage system. You don’t think that there is a hole under your house into which polluted water is drained. This means that all this water needs to be pumped through a centralized pipeline system using pumps to the territory of the water treatment plant. Do you need to pay someone for this? Of course.
What about wastewater treatment plants? This is a completely separate topic . Modern wastewater treatment plants, for example, cost a lot of money for a city with a population of one million. Billions. But it is worth it and investors expect a return on their investment.
This is where the issue of tariffs arises.
Attention Law No. 416 clearly states that the tariff for water supply and sanitation is determined by the authorized body in each region.
What is the basis for setting tariffs? From objective local conditions.
This includes the following components:
- condition of the water supply and sewerage network;
- distances over which water and wastewater have to be pumped;
- condition of pumping stations and equipment thereon;
- number of consumers;
- network maintenance by emergency crews;
- ensuring the functionality of the automated control system;
- payment for water utility workers.
There are other components, but those presented are decisive when setting the tariff.
If you look at the numbers, then water disposal (sewerage with subsequent treatment) in some regions has the following tariff: Yaroslavl region - 18.46 rubles per 1 cubic meter. m. Rostov on Don – 27.45 Moscow – 21.90
Surface drainage system. Surface linear drainage
Surface drainage is mandatory on the site. It removes excess moisture from the site thanks to the installation of point rainwater inlets and trays throughout the entire site. It not only brings benefits, but also looks very beautiful on a site with any design. In just a few years, you will be able to experience material benefits thanks to the installation of a drainage system:
- You will save on home renovations
- Tracks will last much longer
- The service life of the house will also increase
Surface drainage is divided into two types:
- Linear drainage;
- Point drainage.
Linear drainage is capable of draining water over a long area. It is represented by a large trench, which is covered with gratings on top. Thanks to the large trench area, the linear drainage system can be easily combined with roof drainage, thereby saving money on additional pipes.
Linear trenches are made either from concrete by pouring, or they buy ready-made plastic gutters, which are usually sold with gratings, which will facilitate the installation process and significantly reduce its time. Linear drainage can be installed not only in areas with a large area: sometimes, due to convenience, it is installed in small areas.
Advantages of a linear drainage system:
- A small number of hidden pipes are laid, due to which blockages practically do not occur.
- The ability to drain large volumes of water from a large area in a short period of time.
- Easy to install.
- Low cost due to the unnecessary installation of a large number of pipes.
- The system may have the length necessary to drain water.
Recently, for the manufacture of linear trays, a material such as polymer concrete, which contains quartz, has often been used. Polymer concrete has a huge number of positive qualities, among which the most important are:
- High strength, exceeding the strength of conventional concrete several times.
- Does not allow water to pass through.
- Resistant to severe frosts and sudden temperature changes.
- Has high impact resistance. Unlike ordinary concrete, it does not crack or chip due to minor impact.
- The minimum service life of polymer concrete is 30 years.
- It has a fairly smooth surface: water drains faster, debris does not accumulate, but flows into the sewer well.
- Installation takes about a day.
- Polymer concrete pipes have the ability to “combine”, that is, they can be installed at different angles.
Polymer concrete has only one drawback, but it is quite noticeable - it is very expensive and beyond the means of ordinary people.
Plastic gutters and channels are also quite popular. Among their advantages are the following:
- They have high frost resistance.
- Good impact resistance is noted.
- It is not affected by ultraviolet rays and aggressive environments due to the addition of special substances to the composition.
- They are lightweight, making them easy to transport and install.
- No silt forms on the surface of the gutters and water drains very quickly due to the smoothness of the surface.
- During installation, you can easily change the length of the gutter or channel, since it is enough to cut the plastic with a regular hacksaw.
- The pipes are easily connected to each other.
Recently, experts have not recommended installing gutters and channels made of concrete, because concrete is a rather finicky building material. Among its disadvantages are:
- Heavy weight.
- Low impact resistance (at the slightest impact, a piece may break off from the concrete gutter).
- Subject to temperature changes: with large changes it cracks.
- Not frost-resistant, which has a very bad effect in our climatic conditions. In severe frosts, concrete begins to crack and chips appear.
- Water does not drain well due to the high friction of its surface, and silt deposits accumulate on the surface.
We can say that in this area of construction, concrete has already outlived its usefulness. However, it is still quite popular due to its relatively low cost. Many people still use ordinary concrete in the construction of drainage systems.
Advantages of a drainage system
One of the main tasks of a surface drainage system is to drain rainwater away from the house, protect the foundation of the building, and drain water from paths and other buildings. If you have a properly installed drainage system on your site, the service life of your home can be doubled. And all thanks to the fact that drainage systems remove rainwater from the foundation of the building. Also, the presence of a drainage system near the house will reduce the cost of repairing the building, because it is water that causes the plaster to fall off, the paint to peel off, and when the house shrinks due to rainwater, all the plaster can crack, both outside and inside the building. Therefore, if you want to install surface drainage, first think carefully: temporary savings can turn into big problems in the future.
Especially if there is asphalt or paving slab paths on the site, it is recommended to install surface drainage, which can significantly extend the service life of the roads. If water constantly gets on them, then within a year the asphalt will begin to crack due to sinkholes in the ground underneath as a result of being washed away by rainwater, and the paving slabs will most likely completely fall into the ground.