What is a tax deduction?
A tax deduction is a guarantee established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, which can be:
- Reimbursement to a citizen of personal income tax paid in the amount of 13%;
- The legal basis for a citizen’s failure to pay income tax is 13%.
Each of these guarantees has its own advantages. So, having received a large amount of personal income tax refund, you can spend it on something useful. In turn, without paying personal income tax, you can spend the freed-up funds immediately, without waiting for them to depreciate due to inflation.
It is worth noting : which of these 2 guarantees can be used depends on the specific type of deduction. Russian laws establish a fairly large number of them. The most popular ones include:
- property deduction (provided when purchasing residential real estate);
- social deduction (provided when using paid services in the field of education and healthcare);
- standard deduction (provided to certain categories of the population).
All of these deductions are united by the fact that the condition for receiving them is that the citizen has income subject to personal income tax - a tax at a rate of 13%. In general, this tax is charged on wages received by a person under an employment contract.
Can a pensioner receive a tax deduction for treatment in 2018-2019
Many pensioners continue to work after retirement. There are no barriers to receiving a deduction for working pensioners. It is worth noting that we are talking about official employment, which involves the employer withholding and transferring personal income tax of 13% to the budget.
The withheld personal income tax from the specified remuneration amounted to 39,000 rubles. (300,000*13%), which gives her the right to apply for a deduction. The amount spent is 35,000 rubles. less than the limit of 120,000 rubles. Accordingly, it can be taken into account in full. The deduction amount will be 4550 rubles. (35000*13%).
How long do you need to work to receive a deduction?
How long do you need to work to get a tax deduction ?
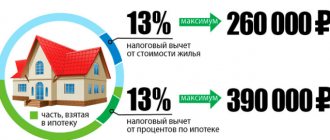
The length of your work experience does not in any way affect the possibility of receiving a deduction. But to a certain extent it can influence its size. For example, a person bought an apartment worth 2,000,000 rubles. After this, he has the right to a deduction in the amount of 13% of this amount - that is, 260,000 rubles.
Let’s agree that a person earns 40,000 rubles a month. Personal income tax is charged on this amount at the rate of 13%, that is, 5,200 rubles. And in order to receive a deduction in the amount of 260,000 rubles, a person needs to work for about 50 months (260,000 / 5200).
In turn, if a person’s salary is 80,000 rubles, then he will need to work for 25 months. If the salary is 20,000, then it’s already 100 months, and so on proportionally.
What documents will be required
To apply for a deduction, you will need a standard package of certificates:
- The applicant's passport and completed application form;
- Correctly completed tax return 3-NFDL for the reporting period;
- Certificate 2-NDFL;
- Other documents (for example, a copy of the purchase and sale agreement if a person claims compensation for the purchase of residential real estate), with the help of which a citizen can prove his right to receive a deduction.
declaration form 3-NDFL
If you have any questions, it is best to seek advice from the territorial tax authority, where they will tell you how to correctly submit documents.
Let's look at the situation using examples.
Example. The man retired due to age, so he resigned from his previous position. In this case, in order to receive a deduction, he can provide information about his income for the last 3 years before termination of employment. According to the law in 2018, tax refunds are possible for 2020, 2020 and 2020. Or he must submit 3-NDFL in his tax return, according to which he has another officially declared current source of income.
Example. Registration of a tax deduction without work. Let’s assume that a citizen did not work for some period of time, then in 2020 he purchased a small apartment on credit, and at the beginning of 2020 he got a job and now officially receives 35 thousand rubles every month. At the beginning of 2020, he has every right to submit the collected package of documents to receive a property deduction.
If a person retires and three years before that he did not have income subject to 13% personal income tax, he does not have the opportunity to exercise his right to receive a tax deduction.
There are other grounds for refusal:
- The declaration is filled out incorrectly or contains incorrect data;
- The applicant has undeclared income;
- The deduction was previously used in full and can no longer be provided.
How to get a deduction without earned income?
How to get a tax deduction if you don't work ? In fact, there are quite a few other sources of income that are taxed at the 13% rate. For example:
- income from the sale of any property (for example, an apartment, a car);
- income from the provision of services under a civil contract;
- income from renting out an apartment.
The application of these incomes for the purpose of obtaining a deduction is carried out according to the same principle as in the case of wages. For example, if a person rents out an apartment and receives 40,000 rubles per month from the tenant, he will have to pay 13% of this amount monthly - that is, 5,200 rubles.
These funds can also be used to receive a deduction - for example, from the amount spent by this person on the purchase of a second apartment. If the housing he purchased costs 2,000,000 rubles, then in order to receive a full deduction from this amount, the first apartment will need to be rented out - as in the case of a salary of 40,000 rubles, within 50 months.
How to get it and where to apply
In order to receive an IC for an unemployed person, you must complete the following steps:
- First of all, you must provide a certificate in form 2-NDFL. This document is provided by the employer or organization where the citizen worked;
- submitting a corresponding notification to the authorized agency. To choose from: territorial tax authorities, multifunctional center or through the employer;
- filling out a certificate in form 3-NDFL. This certificate is a declaration of income received by an individual;
- documents that are notarized confirming expenses incurred for the purchase of housing, education, and medical care. Without documentary evidence of the facts, the deduction will be denied;
- checking the package of documents. The audit can be carried out for up to 3 months by tax inspectors;
- providing details of an individual bank account for the transfer of compensation.
If the tax office makes a positive decision, the funds will be transferred to the account within 30 days.
ATTENTION !!! Refusal is also possible, most often due to incorrectly completed documents. It is worth noting that the 3-NDFL certificate should be filled out in advance in consultation with a lawyer.
Mutual offset of taxes and deductions: a privilege in the absence of permanent income
It is noteworthy that Russian legislation allows citizens to mutually offset deductions and personal income tax. In essence, this is a type of guarantee under which the legal non-payment of this tax is carried out. But it may be especially interesting for people who do not have any regular income taxed at a rate of 13%.
For example, if a person sold an apartment for 2,000,000 rubles, he will have to (if he has owned it for less than 3 years) pay the state a tax of 13% on this amount, that is, 260,000 rubles. But if this person bought another apartment in the same year, also for 2,000,000 rubles, then he will have the right to receive a 13% deduction from this amount, amounting to the same 260,000 rubles.
This citizen can contact the tax office with an application for mutual offset - a deduction of 260,000 rubles, and a tax of 260,000 rubles. As a result, he will not owe anything to the state.
The presence of any permanent income for a citizen to carry out mutual offset of the property deduction - from the amount for the purchase of one apartment, and personal income tax - from the proceeds received from the sale of another apartment, does not matter.
How to get a tax deduction for pensioners for treatment? 4 stages
- if it works;
- if he does not work, but received any income during the reporting period. For example, sold property or rented it out;
- if he does not work and did not receive any other income other than a pension during the reporting period, the pensioner’s spouse or children can receive a deduction.
Answer. In this case, the pensioner can apply for a deduction for himself, or maybe for his working husband or child. Please note that you cannot partially “use” the deduction. The most rational thing to do in case of low income would be to arrange part of the expenses for yourself, and partly for relatives. It is important to take into account that if the deduction is provided to a relative, then documents confirming the right to receive it should be issued to him. In the documents, the patient is indicated as a pensioner, and the payer is the recipient of the deduction.
Features of receiving a personal income tax refund for unemployed people
note
To understand whether it is possible to receive a tax deduction for an unemployed person, you need to find out what kind of benefit it is.
Let's look at a couple of situations to understand the return mechanism:
- Citizen Ivanova paid 100,000 rubles in personal income tax for the year, bought a room for 1 million, and has the right to return 130,000 rubles. But this year she will not return the specified amount, she will be able to receive 100 thousand - exactly as much as she paid to the state, that is, it is her taxes that will be returned;
- Citizen Petrov bought a house for 2 million, 13% of this amount - 260 thousand. But over the past 3 years, he has not paid personal income tax, so it is not yet possible to take advantage of the benefit.
Work experience does not affect the possibility of providing benefits. Even if a person works only for the first month, he will be able to compensate for personal income tax, but only in the amount in which he paid it.
Thus, you will not be able to get a tax deduction if you do not work officially and do not pay personal income tax. In fact, it cannot exist: after all, the money was not included in the budget.
A tax deduction is a special preference that allows an individual to legally reduce the personal income tax base, that is, the amount of taxable income. The use of this benefit leads to a reduction in income tax transferred by the citizen to the budget.
A person receiving a salary on which personal income tax is withheld (13%) has the right to apply for such deductions through his employer or by contacting the Federal Tax Service. The types, grounds and procedure for processing personal income tax deductions are regulated by Articles 218-222 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (TC).
Thus, for residents of the Russian Federation the following deductions are provided:
- Standard deductions (Article 218 of the Tax Code), which are provided to individuals belonging to certain (preferential) categories or having minor children.
- Social deductions (Article 219 of the Tax Code), which are issued in relation to amounts spent by taxpayers on charity, study, purchase of medicines, and medical services.
- Investment deductions (Article 219.1 of the Tax Code), which an individual is entitled to receive for transactions with securities and an individual investment account.
- Property deductions (Article 220 of the Tax Code). They are used for the sale of assets (real estate, cars) and the purchase of residential properties.
- Professional deductions (Article 221 of the Tax Code) for entities engaged in business, private practice, work under civil law agreements, as well as receiving royalties and other similar remunerations.
All preferences listed above are provided to applicants who have proper grounds, subject to the specified conditions (requirements) and in accordance with established restrictions (limits). An essential requirement is that the applicant has income (earnings) subject to personal income tax (13%). The grounds for an individual to receive these benefits, as a rule, require documentary evidence.
Using such a preference, the taxpayer can return only the tax amount that was withheld from the income received for a specific calendar year. In other words, if a citizen does not have official income taxed at 13%, he will not be able to legally apply the personal income tax deduction.
However, the concept of taxable income in this context is not limited to the salary paid to the personal income tax payer at the place of official employment. Obviously, a person who is a tax resident of the Russian Federation and does not work under an employment contract may have other sources of income (earnings):
- proceeds from the sale of assets owned by the deductible applicant. For example, during the tax period, a citizen could sell his own living space or personal car. Personal income tax (13%) is charged in such situations if the seller did not wait for the minimum period of possession of the object (5 years or 3 years);
- income from renting out your own assets. For example, we may be talking about providing a citizen’s personal living space for temporary use to another person on a reimbursable basis;
- receipts from the performance of certain works by an individual on the basis of civil law agreements;
- other income specified in Article 208 of the Tax Code, but not exempt from personal income tax under Article 217 of the Tax Code.
If an unemployed person has received any earnings and paid personal income tax (13%), he can declare these earnings for deduction. For this purpose, he contacts the local branch of the Federal Tax Service with a package of documentation:
- Civil passport of the individual applicant.
- Application with the required content.
- Declaration 3-NDFL.
- Documentary evidence of income received by the applicant and subject to 13% tax.
- Papers that unambiguously prove the citizen’s right to receive the declared benefit (for example, an agreement for the purchase of housing, education or the provision of medical services), as well as payment documentation confirming the payment by the applicant of these expenses.
We suggest you read: How to divorce your wife if you have children or a minor child
It represents a return of money previously paid to the budget in the form of personal income tax or a reduction in the amount that is taxed. This means that the refund is due to those who regularly pay taxes.
All rules, conditions and procedures for processing deductions are regulated by Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Unemployment status can be interpreted in different ways. From the point of view of citizens, an unemployed person is someone who simply does not work. From the point of view of the law, an unemployed person is a person who does not have official employment.
This category includes students, retirees, and people who work without official employment.
It often turns out that a person works, has income, but cannot apply for a tax deduction, since the size of his salary is not officially displayed anywhere, and he does not pay taxes on it.
And a deduction is the return of exactly those funds that a citizen paid to the budget in the form of income taxes. Therefore, if a person does not work officially, it becomes difficult to obtain a tax deduction. However, depending on the situation, the unemployed can still receive benefits from the state.
It is impossible to state unconditionally that an unemployed person cannot claim a deduction, since such a concept has an ambiguous interpretation:
- A person who recently quit his job may be unemployed, but before that he worked and regularly paid personal income tax.
- From the point of view of the law, a person is unemployed, even if he works but is not officially employed.
- A person may have other sources of income, for example, he provides hairdressing services at home, sells something made with his own hands, etc.
- A citizen may not work, but receive income from renting out housing or a car.
Whatever sources of income a person has, if they are unofficial and no tax is paid on them, he is not entitled to a refund of the deduction. But there are other ways to apply for benefits. An unemployed person can get it in the following ways:
- Apply for a refund for the previous three years if he quit recently, and before that he was officially employed. You can return the 13% personal income tax that was paid over the last three years. For example, a person quit in 2020, but in 2020 he was still working. In 2018, he can submit a declaration for the year in which he worked and return part of the funds. In 2020, the right to deduction will already be lost due to the expiration of the statute of limitations.
- Issue a refund for your working spouse. The main condition is that the spouse retains the right to return the deduction.
- Legalize existing sources of income, after which the citizen will have the right to claim a refund of taxes paid.
Important! A person who receives unemployment benefits cannot take a deduction because such social benefits are not subject to income tax.
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for several categories of benefits that are provided in various situations. An unemployed person can apply for only some of them.
Standard deductions. These are benefits that reduce the income tax base.
A citizen receives a salary of 20 thousand rubles, from which 13% of personal income tax is calculated. If he takes advantage of the benefit (if he is eligible), he can reduce his tax base by some amount. For example, he has the right to 3,000 rubles. Every month, personal income tax will be withheld not from 20,000, but from 17,000 rubles.
Standard deductions are issued to a specific taxpayer and only imply a reduction in the tax base.
The benefit is provided throughout life, as long as conditions exist that preserve the right to it. An unemployed person who does not pay any taxes to the budget cannot apply for this type of benefit.
If you have official sources of income, you can reduce the amount that will be taxed.
Social deductions. These are benefits that are provided when receiving paid medical or educational services, as well as when engaging in charity. Social deductions within the established limits can be issued at least every year.
An unemployed person has an excellent opportunity to return part of the money spent through working spouses or parents.
Citizen Pirogova L.D. is a housewife and has not worked for many years. The husband provides for the family. Every year she goes alone to a sanatorium to improve her health. In this case, through her husband, she can return 13% of personal income tax for each year.
Important! The taxpayer has a limit on how much he or she can recapture. A wife can return personal income tax through her husband only if the husband has not used or exhausted the established limit for his own purposes.
Property tax deductions. This type of benefit is provided when buying or selling property.
If an unemployed person buys real estate, it makes no sense to return the tax deduction through a spouse, since a married couple has equal rights to property and the same limit.
It doesn’t matter for whom the working spouse applies for the deduction - for himself or for the unemployed half, his limit will be 260,000 rubles, which he can spend throughout his life when purchasing various real estate.
When selling property, a benefit is provided in the form of a reduction in the tax base. According to the law, a person with official income can submit documents and pay tax not on the entire transaction amount, but minus the established amount, which is equal to 1 million rubles.
When does the right to deduction arise?
There is constant confusion with deductions in the absence of official income: it seems that if there is no white salary at the time of purchase, then there will never be a deduction. Or that the deduction can only be received within three years after the purchase. This is a misconception that causes people to lose money. Let's break it down into pieces.
To qualify for a deduction, all conditions must be met:
- You are a tax resident.
- Apartment on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- There are documents confirming rights and expenses for the apartment.
- The seller is not a close relative of you.
- You have not previously used your right to deduct, or there is a balance.
If these conditions are met, you are already entitled to the deduction. The only question is whether you can immediately return the personal income tax, that is, take advantage of this right.
When can I return personal income tax?
You can only claim a deduction for a tax refund if you have something to return. To do this, you must pay something to the budget - then the state will give you the money. Or you will be charged personal income tax - then you will be allowed not to transfer it to the budget and keep it for yourself.
But you can deal with all issues with tax refunds at any time - even 10 years after purchasing the apartment. If you currently do not have official income and personal income tax is not withheld from it, this does not deprive you of the right to a deduction. You just can't use it yet.
When you have income taxed at 13%, you will claim the deduction and get your tax refund. Or you won’t pay personal income tax until you exhaust the entire limit.
You can even sell this apartment, but you will not lose the right to use the deduction for it. Just wait until the income appears on which you need to charge 13% personal income tax. Even if this happens many years later, submit the documents and get your money. Or this will be done by your spouse, who was on maternity leave in the year the apartment was purchased and was unable to use her part of the deduction.
We've already talked about why the three-year limit doesn't work here. There is no time limit at all for the right to a property deduction. There are restrictions on the period for refunding the tax paid, but it will not prevent you from returning 260 thousand rubles.
The Ministry of Finance has repeatedly confirmed this in official explanations.
Question-and-answer summary
Is it possible to get a tax deduction without having a job?
Yes. But under one condition: if there are other sources of income taxed at a rate of 13%.
Does length of service affect the possibility of receiving a deduction and its size?
It does not affect the possibility of receiving it in any way. The size is affected indirectly, in combination with the size of the salary.
Is it possible to get a deduction without having regular income?
Yes. For example, if there is a mutual offset of property deduction and personal income tax from proceeds after the sale of an apartment.
Russia provides income tax refunds on certain expenses. These include paying for education and treatment, purchasing an apartment or land for building a house, and paying interest on a mortgage. At the same time, it is legally established that only those citizens who pay income tax can receive such deductions.
It turns out that an unemployed person does not have the right to claim an income tax refund.
Can a non-working pensioner receive a tax deduction when buying an apartment?
For example, when selling an apartment for 4 million rubles and purchasing in the same calendar year a residential building located on a land plot for 3 million rubles, the tax will be calculated as follows: 4 million minus 1 million (deduction from an object owned by less than established tenure period, according to clause 2, clause 1, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) minus 2 million (property deduction when purchasing a real estate property) equals 1 million rubles (taxable income base). In such a situation, any resident citizen of the Russian Federation (pensioner, minor, etc.) can take advantage of the property tax deduction upon presentation of the necessary documents confirming the sale and acquisition of the relevant objects.
Pensioners have the right to a property deduction. To receive a deduction, a pensioner must fill out 3-NDFL and transfer the deduction to the last 3 years. If you continue to work after retirement, it is possible to carry it over to past years and to future years in the general manner.