Who has the right to inherit?
Current legislation does not impose age restrictions. The number of years lived has no legal meaning. A will for a minor is drawn up at any age from the date of registration and registration with the registry office. The only mandatory requirement for drawing up a will is the fact of being born alive.
The heir will be able to become the full owner of the property after reaching the age of majority, when he turns 18 years old. Writing wills for minors is a common practice, which is based on specific articles of the Civil Code.
The order of inheritance by law
The legislation determines the priority for making claims under a will for property left behind by deceased family members. The orphan receives everything that the parents owned, regardless of whether they were legally married. The will does not leave young citizens (minors) without housing, with which they must be provided.
Parents living without marriage registration are responsible to their children. A distinctive feature characteristic of entering into an inheritance: after the death of their fathers, minors (children) are not deprived of the right to claim the wills of other deceased relatives.
The laws are designed so that the interests of the child are protected as much as possible. Therefore, the son and daughter are considered to be the primary claimants under the will. But when drawing up a will for an apartment, grandchildren, bypassing adult children, must sign and certify the corresponding document, on the basis of which they enter into inheritance after the death of the testator.
How to challenge a will for an apartment?
You will also need supporting documents:
- certificate-explication from the BTI;
- a certificate from the BTI on the valuation of the apartment;
- extract from the Unified State Register;
- an extract from the personal account about arrears for rent, telephone, and other utility bills.
It is impossible to enter into an inheritance if any of the above documents (except a will) are missing. When the complete package of documents for obtaining a certificate of inheritance has been collected, you can go to the notary. Stage 3. Contacting a notary If the heir was permanently registered together with the deceased and there are no other heirs registered jointly with the testator, he can continue to live in the apartment and not rush into registering the inheritance. In such cases, you can file cases without meeting the established deadlines. If there is no permanent registration with the deceased, you need to prepare documents and go to a notary.
Inheritance by minors under wills
Spouses and their parents most often make wills for children and grandchildren. The fact of legal capacity at the time of signing the expression of will and the absence of coercion are considered mandatory. Persons incapacitated are not allowed to sign a will.
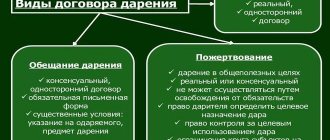
The concept of a will, its form
Legally, a will is an officially executed and notarized document that sets out a strong-willed decision to transfer values (in whole or in part) to a specific person. Mandatory condition: the testator must be the current owner of the material assets specified in the will.
According to the law, a will is a transaction concluded unilaterally. Minor heirs do not sign anything. Only notarization is required. The will is revealed when the former owner is already dead. The fact of death is fundamental in determining the timing.
Will for an apartment
Sometimes several people own a home. Unhindered acceptance of an inheritance for minors occurs when the testator was the sole owner of the home, otherwise the object of the will is the share of living space assigned to him. These are square meters, personal belongings, money or an equivalent to the cost of the housing due.
It is difficult to challenge the decision. By making a will, people provide their minor children and grandchildren with living space, solving the heir’s problems with purchasing real estate in the future. Features of registration - presence of a certificate of the owner, personal presence in the notary's office, payment of the state fee.
The text of the will indicates the address, footage, number of premises and other information about the object of the transaction. If there are several owners, it is necessary to describe the bequeathed share. When the apartment is divided in kind, no problems arise; otherwise, the square footage assigned to the testator is indicated, which forms his part of the total living space.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main legislative act, the Constitution, allows you to dispose of your own real estate. Is it possible to write a will for a minor child? It is possible, and this fact means that:
- The applicant will become the absolute owner of real estate or valuables.
- No one will be able to appeal the decision even in court without compelling reasons.
- Scandal among those claiming values is excluded.
- The order of distribution is determined legally during life.
When making a will for a minor child, the pros and cons must be weighed carefully. Circumstances change, and in order to change the conditions, you will have to spend a state fee and spend time on re-registration.
Another disadvantage is the inability to take possession immediately. For this purpose, a deed of gift is issued for a minor. The birth of another child often becomes the reason for the desire to change the previously signed text of the will. But the state gives all children the same opportunities, regardless of the order of birth, and shares that are unchanged.
The concept of a mandatory share
Everyone who has not reached the age of majority automatically becomes a claimant to half of the bequeathed estate, property values and savings. In case of compulsory inheritance, a minor child enjoys the protection of the state provided for in Article 1149 of the Civil Code. A newborn is regarded as an equal citizen.
In each case of registration of inheritance, all circumstances are considered individually, and if there are two or more children, all of them have equal rights from birth. Therefore, when drawing up a will, it is necessary to take this aspect into account, so that later people do not waste money, time and nerves on litigation. The state determines a mandatory share for each newborn, either with or without a will.
Situations when the court does not side with the applicant rarely occur, but in practice it does happen. By law, the obligatory share is abolished or reduced if:
- There is a legal successor (under the will) who lives on the bequeathed area. This category includes property assets used to generate income (cars, production equipment, workshops, tools, etc.). Grounds – Part 4 of Art. 1149 Civil Code.
- The heir is declared unworthy. These are people who carried out unlawful actions towards the testator in order to obtain valuables. This also includes attempts to increase your share. Basis – Art. 1117 Civil Code.
In the first case, the court evaluates the property and financial status of the applicants and makes a decision that maximally ensures the safety of the obligatory share. In the second, the decision contains a complete refusal to implement the requirements. Often the judge finds elements of a criminal offense. In any case, a recalculation is made or a resolution is issued stating that the request is not satisfied.
The size of the will is calculated from the position of the volume of material assets due to the heirs if there is no will. In this case, the entire list is taken into account - these are the first-priority applicants (conceived children, spouse), as well as relatives by introduction (grandchildren, nephews). Everyone who can prove their relationship has equal rights.
This volume is formed from values that were not bequeathed. But if their value is not enough, the bequeathed property is included in the calculation by reducing the share under the will. The mandatory portion is assigned by the court, which will determine its size and be able to refuse to satisfy the plaintiff’s claim. When it is a minor, this rarely happens.
Contest a will for an apartment
Distribution of shares in the inheritance If the testator does not have a will, the apartment that belonged to him is divided between relatives. The law provides for eight lines of succession:
- parents, spouse, children;
- siblings, brothers, grandparents;
- aunts, uncles;
- great-grandparents;
- cousins, grandchildren, grandparents;
- great-great-granddaughters, great-grandchildren, nephews, nieces, aunts, uncles;
- stepsons, stepdaughters, stepfathers, stepmothers;
- disabled dependents.
The intended heirs of each subsequent stage will be able to receive a share in the apartment if the heirs of the previous stages refused their share or are no longer alive.
When inheriting by law, the fact of the presence of heirs of disabled people, pensioners, and minors is not taken into account.
Peculiarities of the procedure for inheritance by a minor
Before reaching the age of majority, a person cannot sign legal documents. But this does not mean that children are disadvantaged in any way: transactions are formalized by their parents, guardians, adoptive parents, acting on behalf of the wards. In litigation, the interests of children are protected by trustee bodies or persons responsible for education.
A reasonable question arises about how to enter into an inheritance for a minor child when his signature does not have legal force? Can trustees or guardians dispose of the portion due? The procedures for inheritance by minor children have their own characteristics, and no one has the right to make any decisions regarding the object of the claim.
If the teenager has already been issued a passport, then a birth certificate is not necessary, but it is better to take it with you in case you have to confirm the presence of family ties. When it comes to the actual will, this is not required, since all the information to identify the applicant is in the text, and one passport is enough. Photocopies are also valid.
But this does not mean that the young man has the right to immediately sell what he receives. He can sign a purchase and sale agreement only after he reaches the age of majority, and until that moment the property will be registered with him, and responsibility for its maintenance will fall on those who care for the child until he turns eighteen. Legal representatives cannot sell or exchange real estate, or rent out housing, since they do not have sufficient rights to do so.
Required documents
To go through the procedure for taking possession, you must contact a notary office. The applicant is a parent, guardian, trustee. You need to have with you:
- Papers stating that the applicant has the authority to represent the interests of the ward.
- A previously executed notarized will, if available.
- Documentary evidence of family ties confirming the legitimacy of the claims.
- Birth certificate of the heir.
Copies of all documentation are being prepared. You must also have the originals with you. A civil passport serves as identification.
A problem arises when the father is not listed on the certificate. If the parents did not legalize their relationship, and the child’s father was not included in the birth certificate, you will have to prove that the deceased citizen is the father. For this purpose, witness statements, DNA tests, etc. are presented. Judicial practice shows that such cases are resolved in favor of actual paternity.
Filing an inheritance application
You must appear at the notary's office. This must be the office in which the will was drawn up. Then everything can be resolved in one visit. Otherwise, you must obtain the original signed will. There are a number of restrictions:
- It is necessary for the testator to express his own will.
- Six months must pass after the death of the testator.
- A child conceived but not born is not a legal entity.
- The application is written by authorized people.
- Papers are subject to notarization.
If the fact of birth is confirmed, a certificate has been received, and all documentation is available, a sample application can be downloaded on the Internet or obtained from a notary.
It describes everything that the applicant is applying for. A list of documentary evidence of the fact of voluntary transfer at the request expressed during life is provided. The day of compilation, place, signature with transcript are required attributes. All this is certified by a notary. An identification number is assigned and the data is entered into the register.
Conducting inheritance business by proxy
The fact that a child enters into an inheritance involves the preparation of legal documents. The procedure can be entrusted to a professional lawyer. To legitimize his powers, you need to write an appropriate power of attorney and have it certified by a notary. The text indicates the boundaries of authority:
- drawing up statements on behalf of the principal;
- filing claims and petitions;
- representation in court and government bodies;
- other.
In the case of a minor, the principal is a parent, guardian, or trustee. When registering a power of attorney, you will have to pay the state fee determined by Article 333 in paragraph 24 of the Tax Code. The receipt is an integral part of the applications, the list of which is indicated in the corresponding section of the text.
Simplified procedure for inheritance
No one has the right to evict children from housing if they lived at the specified address until the death of the testator. If there are no wills for apartments for a minor child, he will go through the procedure according to a simplified procedure. In basic aspects it is identical to the standard one with the exception of a few characteristic features.
The procedure involves an expert assessment of the value of the inherited property. In this case, there is no state duty. Minor children are exempt from paying, which simplifies entry. When registering through a proxy, it is necessary to notify the guardianship and trusteeship authorities. All permits are documented.
Deadline for inheritance
In this aspect, they are guided by generally accepted legal norms that determine the six-month period. During this period, you can register ownership of the property under a will. 6 months are given to collect documentation, pay state fees, file an application or claim in court. However, there are a number of cases when the procedure does not require the presence of adult representatives.
The beginning and end of this period are stipulated by Articles 191 and 192 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The first day is the date of death of the testator indicated on the death certificate. From that same day, the inheritance is considered open, and all applicants can make claims to the property assets owned by the deceased.
In cases where it is impossible to establish the exact date of death, when calculating the entry period, the date determined by the court is taken as the beginning of the period for disclosing the will. Paragraph 3 of Article 45 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that if there is no such date in the resolution, you should be guided by the day when it came into force. In any case, the period is calculated in a six-month period.
Difficulties arise when property is divided according to a will drawn up by a missing person. The person is listed as alive, but in fact he is not. For such cases, there is a separate procedure for declaring him dead after a specified period. The final confirming order is the court decision.
When can a teenager under 18 years old independently accept an inheritance?
Having a will in hand for a minor grandchild, you can initiate the entry process, even if the age of majority has not occurred. A teenager can do this on his own if he:
- created his own family and is legally married;
- is an entrepreneur, conducts business and pays taxes;
- received a court conclusion on recognition of legal capacity.
If you need to ask questions to a lawyer, write your question in the online communication form for free. Each situation is individual and requires separate consideration.
Missing the deadline for entering into inheritance
There are clear boundaries within which it is permissible to submit claims for recognition as an owner. For six months, parents, guardians, trustees of the minor, as well as other applicants will not be able to dispose of the property. But if 6 months have passed since the opening of the will, and the property has not been received, you need to use a mechanism that allows minors to restore the statute of limitations and challenge the entry, which occurred without the knowledge of the heir.
The procedure involves filing a claim with the court at the location of the inherited apartment (drawing up a will) or the minor himself. A testamentary assignment is considered if the omission is caused by objective reasons, including:
- the minor’s inability to learn about the death of the testator in a timely manner;
- residence of a minor outside the state or in another region of the country;
- illness suffered by the minor, which temporarily limited the applicant’s capabilities;
- inaction of guardians and trustees of a minor due to ignorance of family ties, etc.
In addition to information about the heir, the statement of claim of a minor indicates the object of the dispute under the will, information about the defendant, and also provides the evidence base confirming the right of claim. The result of the proceedings may be:
- Leaving without consideration if the court does not find legal grounds for conducting a judicial process to consider the minor’s claim.
- Full or partial satisfaction of the applicant’s demands with the transfer of property into ownership or payment of an equivalent amount to the minor.
- A settlement agreement, if minors living at the address indicated in the claim, agreed with the plaintiff on mutually beneficial terms.
The complaint is written by representatives of children until they reach adulthood. Laws protect the interests of teenagers who do not have official parents.
Demographic growth
The will of Canadian lawyer Charles Millar, who died in 1926, caused a real sensation in society. It was not only original, but also influenced the demographic situation in the state:
- he bequeathed quite profitable shares of the hippodrome to his friends who opposed gambling;
- to other friends who had spent their entire lives fighting for social sobriety, he left shares in the brewery;
- The lawyer left a luxurious mansion in Jamaica to his acquaintances who hated each other, subject to shared use;
- He promised to pay a huge sum of money to any Toronto resident who gave birth to the most children within 10 years of Millar's death.
As a result, from 1926 to 1936, Canada experienced a real population explosion. In the hope of a rich inheritance, women willingly gave birth to children. The winners were 4 ladies who were able to give birth to 9 babies in 10 years. They split the $500,000 equally. However, after this, no more children were born into their families.
Rights of illegitimate, adopted and stepchildren
The basis for legislative acts is the equality of rights of minor children born into the world. Therefore, even if it is an unofficial spouse and adoptive parents, a minor has the right to use the will with the same chances as his own children. If paternity is indicated on the birth certificate, this is a sufficient basis.
Adoption is an optional condition. It is enough that the minor has been a dependent for more than 12 months. The presence of two disinterested witnesses in court (neighbors, relatives) who can confirm this fact is a sufficient reason to recognize the right to be a minor adoptive parent if the adoptive parent has died.
Adopted minors immediately after registration acquire the same opportunities as those born by birth. The requirements of the will are lawful and unshakable, since from the point of view of legislation, all minors become relatives. All descendants who will be born from adopted citizens can claim what remains after the death of their adopted grandparents.
Will for a stranger
Indeed, a notary should talk to a person who wants to draw up and certify a will and ask whether he really wants to bequeath property not to relatives, but to strangers. After the conversation, the notary makes subjective conclusions about the sanity of the person. But he does not have knowledge in the field of psychiatry and medicine and cannot conduct an expert assessment of sanity. Accordingly, the conclusion made by the notary about the testator’s understanding of the meaning of his actions can be challenged in court.
However, the contesting party must prove the existence of relevant grounds, in this case - “vice of will” on the part of the testator. The fact that the will was drawn up in favor of a stranger will not be of significant importance.
Your task is to prove that when signing the will, your grandmother was not in charge of her actions and did not understand their consequences.
Refusal of inheritance
Becoming the owner of inherited objects is not an obligation. If this could cause harm to a minor, representatives have the right to refuse to join. Along with property of value, the will accepts debts that are associated with the object of the transaction.
In this case, it makes sense to refuse and throw off the burden of debt. Refusal to join is a procedure that requires the presence of a permit document that is issued to minors by the guardianship authorities. You can make such a decision personally from the age of 14. Documentary evidence of permission from the guardianship authorities, parents or persons replacing them will be required.
You can refuse in favor of:
- other adult and minor citizens specified in the will;
- other minor heirs of any order by relationship;
- minors acting by right of representation (nephews, grandchildren);
- minor relatives acting as hereditary transmission.
The last paragraph involves minors inheriting property belonging to a deceased person who did not have time to officially assume the rights of the owner under the will. Some cases suggest that the minor in whose favor the waiver is issued falls under two or more categories of legal successors. A refusal on one occasion does not exclude the existence of rights based on other circumstances.
It is impossible to foresee the situation of refusal of a will in advance. While the minor testator is alive, the procedure cannot be initiated, as specified in the Civil Code. When the subject of the proceedings is public housing, neither adults nor minors can refuse.
A complete list of minors in whose favor property can be transferred under a will is given in paragraph 1 of Art. 1158 Civil Code. It is impossible to give property to incapacitated people, since they will not be able to formalize inheritance. The transfer procedure for minors is carried out in the presence of a notary and involves drawing up an appropriate application and notarization. The text indicates all interested parties, the object of the transfer, the place of compilation, and the date.
The procedure for drawing up and executing a will
A testator may draw up a will in favor of a minor if its contents do not contradict the provisions of the law. If the contents of the will were known before the death of the testator, its terms do not suit other claimants; the possibility of challenging it appears only after the death of the owner.
There is a generally accepted procedure for paperwork:
- The document is drawn up in writing and certified by a notary;
- The paper is prepared in two copies. Can be handwritten or printed. Certified by the signature of the property owner;
- One copy each remains with the notary and the owner;
- The document can be open or closed;
- It is recommended that witnesses be present during compilation;
- The specified procedure for disposing of property may not be disclosed until the death of the testator.
The document must contain the following information:
- Date, place of compilation;
- Information about the testator;
- Information about heirs;
- Full information about inherited property;
- The testator's signature;
- Notary's signature, seal.
After drawing up and certification, data about the document is entered through a unified notary register. You can find out about the existence of a document from any notary in the Russian Federation.